Figure 6. Roscovitine administration mitigates cisplatin injury in Fan1 KO mice.
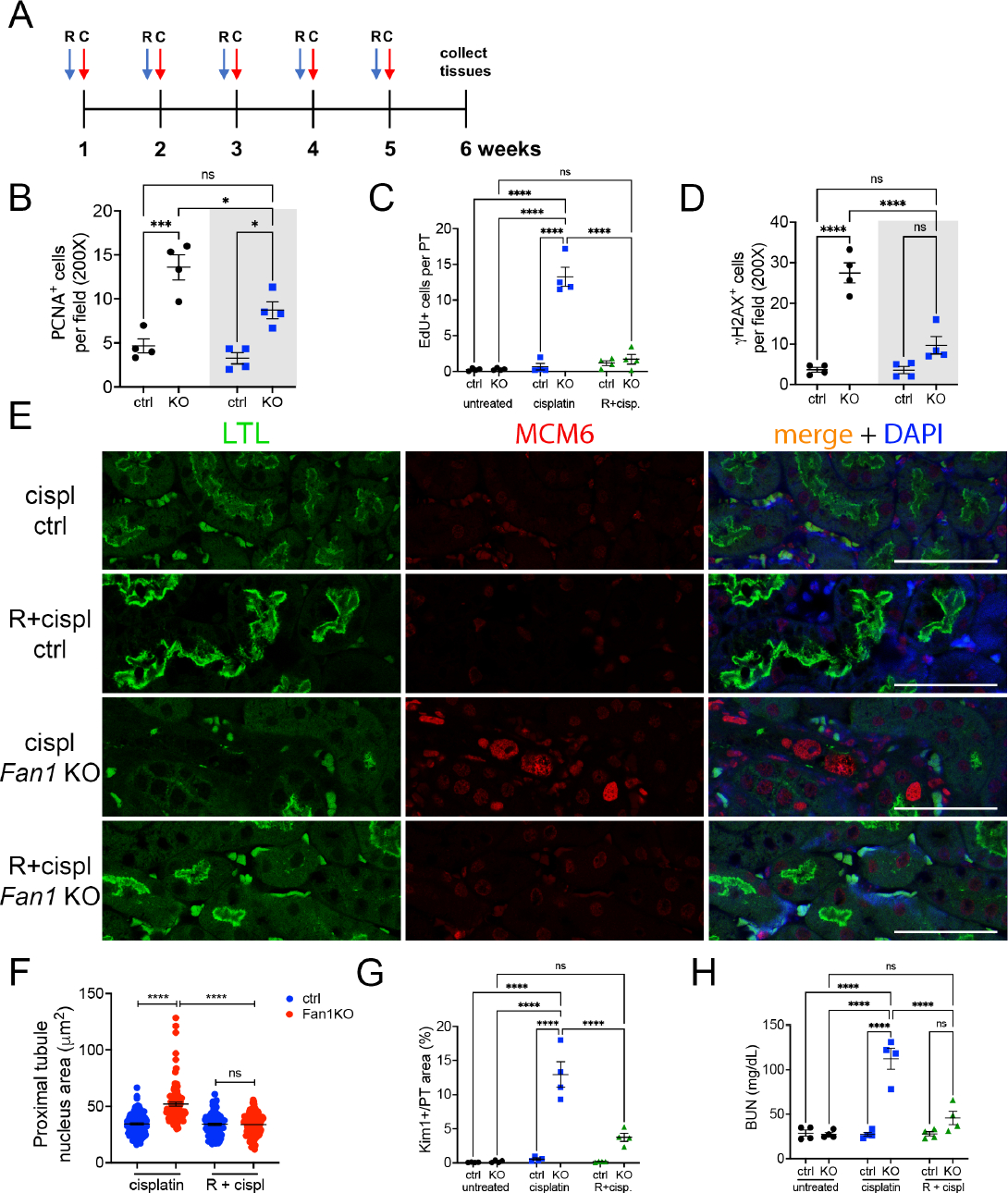
(A) Overview of roscovitine and low dose cisplatin administration protocol. Roscovitine (150 mg/kg) was administered via ip 1 hour before cisplatin (2 mg/kg), and tissues collected on week 6 after the start of the procedure. R – roscovitine, C – cisplatin.
(B) Quantification of PCNA-positive cells in cisplatin and roscovitine/cisplatin treated kidneys reveals that roscovitine treatment blocks S phase cell cycle activity in cisplatin-treated Fan1 KO mice (n=4 mice; *p<0.01, ***p<0.001).
(C) Quantification of EdU-positive cells in cisplatin and roscovitine/cisplatin treated kidneys reveals that roscovitine treatment effectively blocks DNA replication in cisplatin-treated Fan1 KO mice (n=4 mice; ****p<0.0001).
(D) Quantification of γH2AX-positive cells in cisplatin and roscovitine/cisplatin treated kidneys reveals that roscovitine treatment reduces DNA damage in cisplatin-treated Fan1 KO mice (n=4 mice; ****p<0.0001).
(E) IF staining of LTL (green) and MCM6 (red) in cisplatin and roscovitine/cisplatin treated Fan1 KO kidneys. Roscovitine treatment blocks the expression of MCM6 and the formation of karyomegalic nuclei in Fan1 KO proximal tubule cells. Scale bar 50 μm.
(F) Quantification of the nuclear area in proximal tubules of cisplatin and roscovitine/cisplatin treated kidneys demonstrates that roscovitine treatment prevents karyomegaly in Fan1 KO kidneys (cisplatin ctrl 34.4±0.9; cisplatin Fan1 KO 51.9±1.7; R+cispl ctrl 34.1±0.9; R+cispl Fan1 KO 33.7±0.9; ****p<0.0001, n=100 nuclei each).
(G) Quantification of KIM1-positive area in proximal tubules demonstrates that roscovitine administration leads to significant reduction in KIM1 expression in cisplatin treated Fan1 KO kidneys (cisplatin Fan1 KO 12.9±1.9% vs R+cisplatin Fan1 KO 3.7±0.6%, ****p<0.0001), n=4 each.
(H) Blood urea nitrogen measurements in control, cisplatin treated, and roscovitine/cisplatin treated mice. Roscovitine improves kidney function in cisplatin treated Fan1 KO mice, (n=3–4 each; ****p<0.0001).
(B,C,D,G,H) Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. A 2-way ANOVA with Tukeys’ post hoc analysis.
