Figure 3.
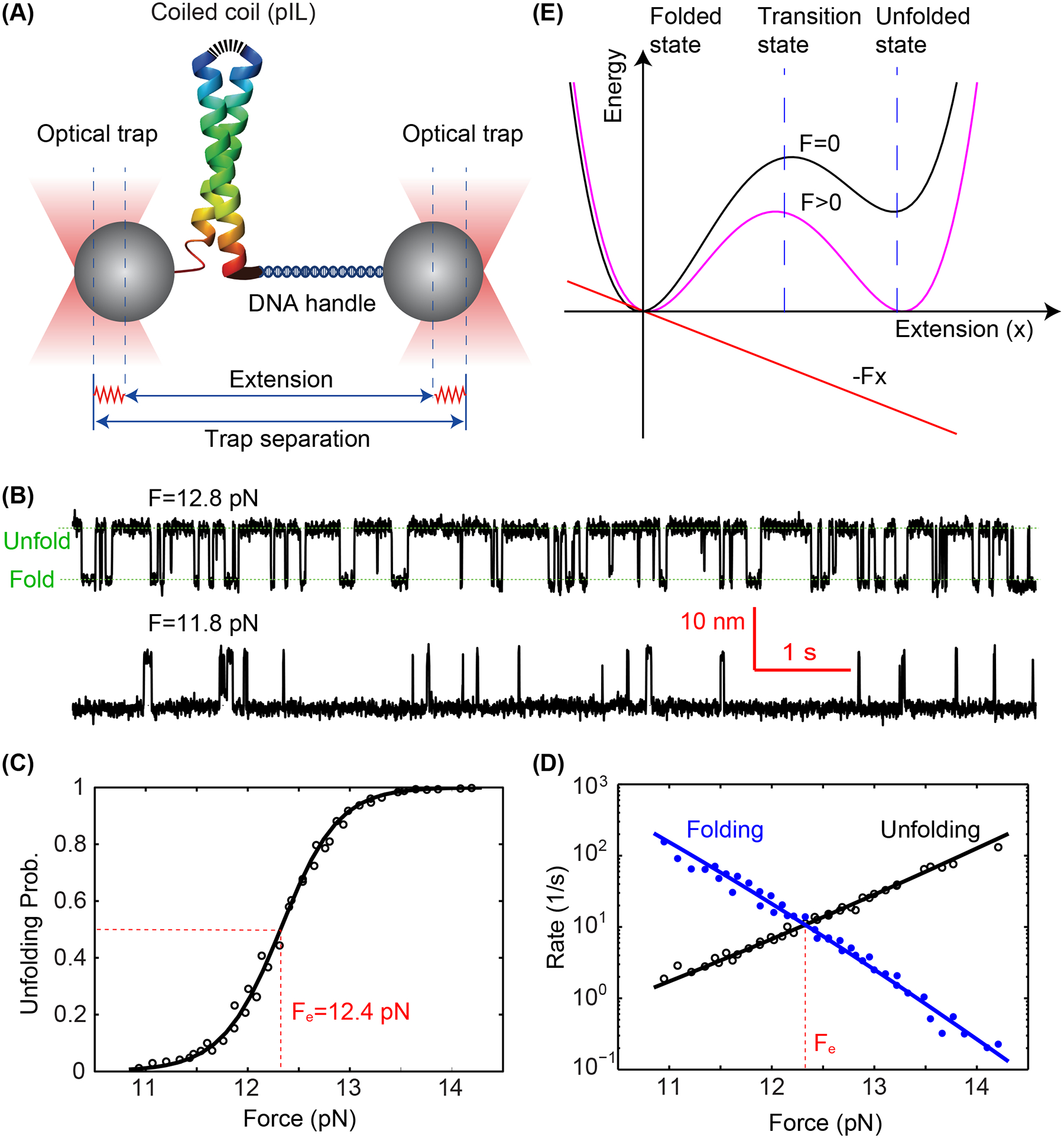
Folding energy and kinetics of a strong coiled coil revealed by optical tweezers. (A) Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. The homodimeric GCN4 variant is crosslinked at its N-terminus (top) and pulled from its C-terminus via a DNA handle. The force applied to the protein is controlled by the separation between two optical traps and the extension of the protein-DNA tether is measured to probe protein folding and unfolding transitions with subnanometer and submillisecond resolution. (B) Time-dependent extensions due to reversible unfolding and refolding of the coiled coil at two constant forces (F). (C) Unfolding probability of the coiled coil as a function of force, with the measured values and theoretical predictions shown in symbols and the line, respectively. The reversible folding transition has an equilibrium force of Fe=12.4 pN as indicated. (D) Measured folding and unfolding rate (symbols) and their theoretical predicts (lines) as a function of force. (E) A constant external force (F) applied to the protein tilts its folding and unfolding energy landscape to facilitate protein unfolding. Specifically, the force lowers the energy of the unfolded state and unfolding energy barrier in their extension-dependent manner.
