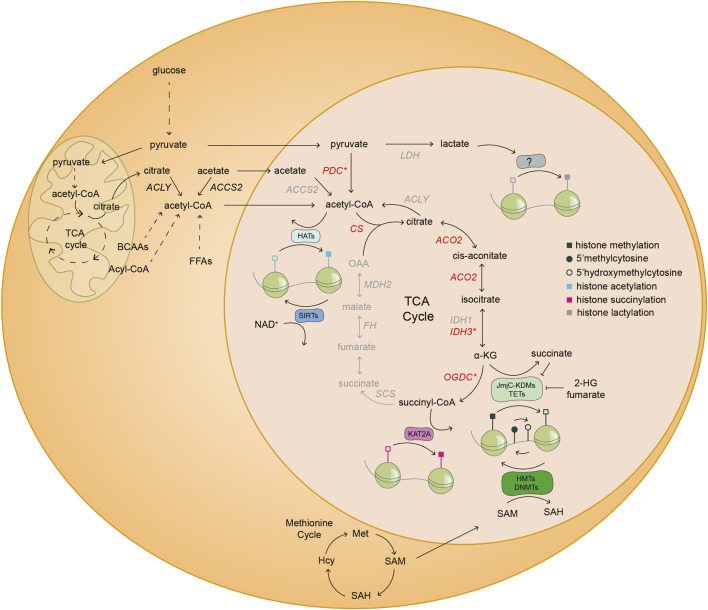
FIGURE 2.
Nuclear metabolism shapes the cellular chromatin landscape. Schematic illustration of the coupling of nuclear metabolism with epigenetics. The existence of a nuclear metabolic sub-network of the TCA cycle (black) and nuclear localization of distinct metabolic enzymes (red) have been reported in mouse embryos and/or mESCs. The asterisk (*) denotes that at least one of the subunits of the highlighted enzymatic complexes are found inside the nucleus of mouse embryos and/or mESCs. Specifically, PDH in the case of PDC; IDH3G from the IDH3 complex; and OGDH subunit from the OGDC. The other half of the TCA cycle and several other metabolic enzymes (grey) have only been described in the nucleus of cancer cells. The TCA cycle metabolite α-KG is a co-factor and substrate of JmjC-KDMs and TETs, which are histone lysine demethylases and DNA demethylases, respectively. Conversely, other TCA cycle intermediates, such as fumarate and succinate, and the metabolite 2-HG, are inhibitors of JmjC-KDMs and TETs. SAM derived from one carbon metabolism is a cofactor of HMTs and DNMTs, which add methyl groups to histone lysine residues and DNA, respectively. The complex OGDC catalyzes the conversion of α-KG to succinyl-CoA, which is used by KAT2A to succinylate specific histone residues in cancer cells. Acetyl-CoA derived from various metabolic reactions is used by HATs to transfer acetyl groups to histones. On the contrary, SIRTs consume NAD+ to deacetylate histone residues. Finally, lactate derived from anaerobic glycolysis might be used by yet undescribed epigenetic modifying enzymes, for histone lactylation. ACCS2, acetyl-CoA synthetase 2; ACLY, ATP-citrate lyase; ACO2, aconitase 2; α-KG, alpha-ketoglutarate; BCAAs, branched-chain amino acids; CS, citrate synthase; DNMTs, DNA methyltransferases; FFAs, free fatty acids; FH, fumarate hydratase; HATs, histone acetyltransferases; Hcy, homocysteine; IDH1, isocitrate dehydrogenase 1; IDH3G, isocitrate dehydrogenase 3 subunit G; JmjC-KDMs, Jumonji C-domain lysine demethylases; KAT2A, lysine acetyltransferase 2A; KMTs, lysine methyltransferases; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MDH2, malate dehydrogenase 2; Met, methionine; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; OAA, oxaloacetate; OGDC, oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex; PDC, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine; SAM, S-adenosyl-L-methionine; SCS, succinyl CoA ligase; SIRTs, sirtuins; TETs, ten-eleven translocation methylcytosine dioxygenases; 2-HG, 2-hydroxyglutarate.