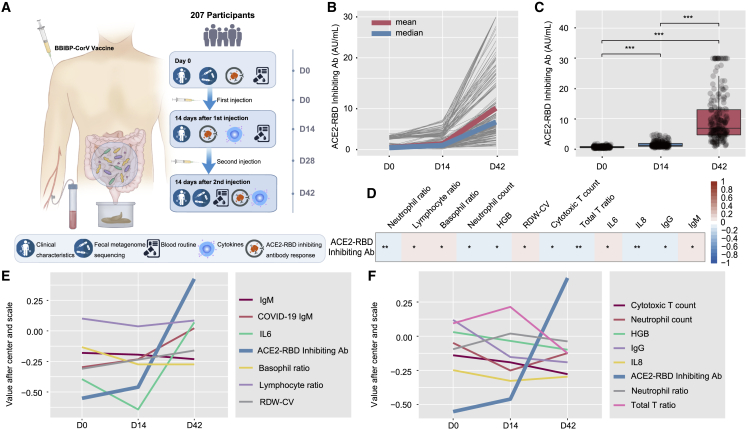
Figure 1.
Clinical characteristics and antibody response
(A) Schematic diagram of the experimental design.
(B) Levels of the ACE2-RBD inhibiting antibody of each participant at baseline (day 0), after the first injection (day 14), and after the second injection (day 42) (n = 207).
(C) Comparison of ACE2-RBD inhibiting antibody levels between days 0, 14, and 42 (n = 207). p values were determined by Welch ANOVA Games-Howell’s multiple comparisons test.
(D) Correlation of ACE2-RBD inhibiting antibody levels and clinical features by calculating the Pearson correlation coefficient between ACE2-RBD inhibiting antibodies (Abs) at days 0, 14, and 42 and clinical features at days 0, 14, and 42 (n = 207). Red represents the positive correlation. Blue represents the negative correlation. p values were determined by Pearson correlation analysis with FDR corrected.
(E) The variation trend of clinical parameters that were positively correlated with ACE2-RBD inhibiting antibody levels at days 0, 14, and 42. p values were determined by Pearson correlation analysis with FDR corrected (n = 207).
(F) The variation trend of clinical parameters that were negatively correlated with ACE2-RBD inhibiting antibody levels at days 0, 14, and 42. p values were determined by Pearson correlation analysis with FDR corrected. n = 207. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.