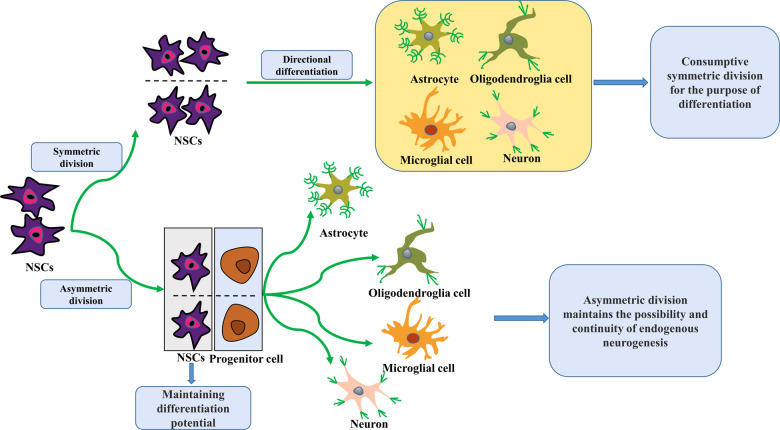
Figure 1.
Schematic of NSCs division and differentiation. NSCs proliferate and differentiate by symmetrical and asymmetrical division. In the adult brain, they usually undergo symmetric divisions to promote self-proliferation or directed differentiation. Over time, this increasing number of expendable symmetric divisions for differentiation purposes will result in a gradual NSCs reduction, leading to a lack of spontaneous endogenous neurogenic repair capacity after brain injury. In contrast, asymmetric division maintains the possibility and continuity of endogenous neurogenesis because it retains NSCs with differentiation potential. NSCs, neural stem cells.