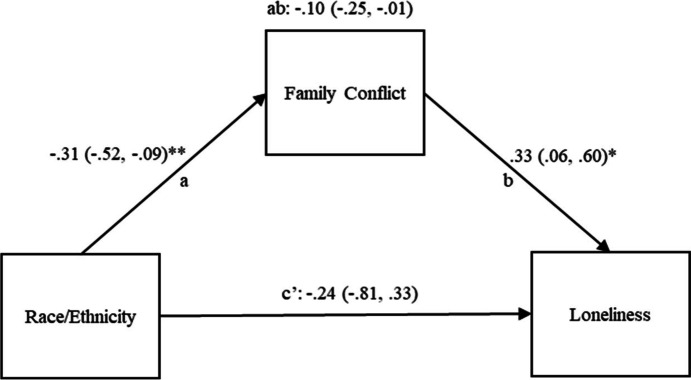
Fig. 2.
Relation between family conflict and early-pandemic loneliness for hispanic adolescents relative to white adolescents. Note: Race/Ethnicity = Self-reported race/ethnicity; Family conflict = Negative interactions factor of the Network of Relationships Inventory: Behavioral Systems Version – Short Form (NRI: BSV-SF; Furman & Buhrmester, 2009); Loneliness = Early pandemic loneliness measured using three items adapted from the Roberts Version of the UCLA Loneliness Scale including the prompt “Since learning about the Corona Virus, have you felt the following” (Roberts et al., 1993); Values in parentheses represent the lower limit and upper limits of 95% confidence intervals. Coefficients and confidence intervals represent unstandardized values. *p < .05; **p < .01