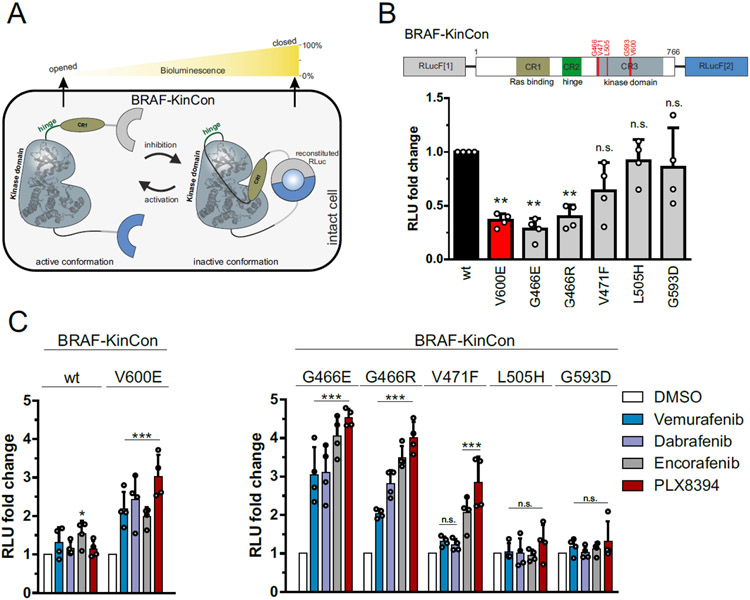
Figure 3. KinCon biosensor results for Resistor-predicted mutants.
(A) Schematic depiction of Renilla luciferase (RLuc; F1: fragment 1, F2: fragment 2) PCA-based BRAF kinase conformation (KinCon) reporter system. Conformational rearrangement of the reporter upon (de)activation of the kinase are indicated. Closed kinase conformation induces complementation of RLuc PCA fragments resulting in increased RLuc-emitted bioluminescence signal. (B) Domain organization of the BRAF-KinCon reporter (top) and basal bioluminescent signals of the BRAF-wt (black), V600E (red), and Resistor-predicted mutant (grey) KinCon biosensors. Bars represent the mean signals, relative to BRAF-wt, in relative light units (RLU) with SD of four independent experiments (nodes). Raw bioluminescence signals were normalized on reporter expression levels, determined through western blotting. Asterisk indicates level of significance versus the wild type BRAF biosensor. (C) BRAF-KinCon biosensor dynamics, induced via treatment with respective BRAFi (1μM for 1h) prior to bioluminescence measurement. BRAF wt and V600E KinCon variants serve as control (left). The Resistor-predicted mutants are shown in a separate bar chart (right). Bars represent the mean signals, relative to the DMSO control, in relative light units (RLU) with SEM of four independent experiments (nodes). All experiments were performed in HEK293T cells 48 hours post transfection. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n.s., not significant by t-test.