Table 1. Resistor correctly identified 8 resistance mutations in EGFR to erlotinib, gefitinib, and osimertinib.
For osimertinib, G796R, G796S, G796D, and G796C were on the Resistor-identified Pareto frontier. L792H was in the 2nd Pareto rank. For erlotinib, both T790M and G796D were on the Pareto frontier. For gefitinib, T790M was also on the Pareto frontier. Previous studies have documented all of these resistance mutations as occurring in the clinic (Helena et al., 2013; Avizienyte et al., 2008; Chen et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2018; Ou et al., 2017; Fairclough et al., 2019; Li et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2018; Zheng et al., 2017). † indicates that Resistor predicted the mechanism of resistance to be improved binding of the endogenous ligand to the mutant. # indicates that Resistor predicted the mechanism of resistance to be decreased binding of the drug to the mutant. Note that these predicted mechanisms are only attributed here if the predicted change in the log10(ΔK*) ≥ 0.5.
| Resistor Identifies Clinically-Relevant Resistance Mutations in EGFR | ||
|---|---|---|
| Osimertinib | Erlotinib | Gefitinib |
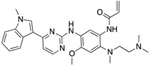
|
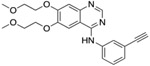
|
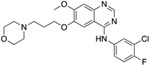
|
| L792H# | T790M†# | T790M †# |
| G796R†# | G796D# | |
| G796S# | ||
| G796D# | ||
| G796C# | ||
