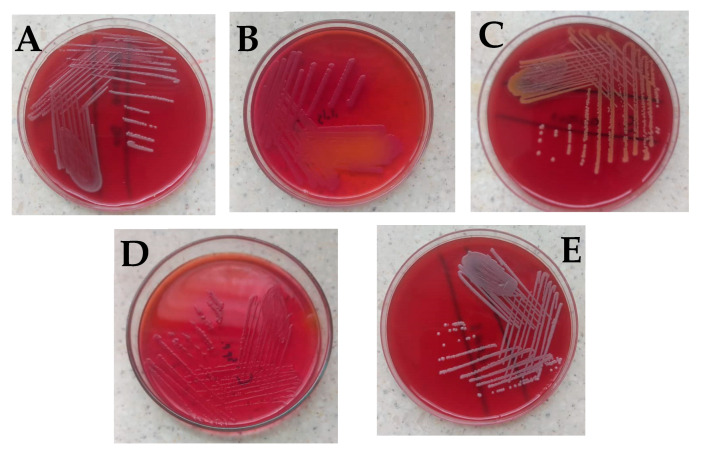
Figure 1.
Bacterial isolates observed in the study. (A) Bacillus cereus on blood agar showing gray round colonies, with varying morphologies of low convex to convex, entire, and were mostly rough, granular, or ground glass in appearance. (B) Citrobacter freundii on MacConkey which showed small pink smooth colonies with partial lactose fermentation (C) Staphylococcus aureus with golden yellow colonies on blood agar (D) Citrobacter spp. on MacConkey which appeared as non-lactose fermenter up to 24 h; however, after 48 h colonies turned light pink, and (E) coagulase-negative Staphylococci showing small whitish round colonies on blood agar which was identified to be Staphylococcus hominis. Identification of the isolates was based on colonial morphology, Gram staining, and a battery of biochemical reactions such as the triple sugar iron test, catalase test, urease test, indole test, and citrate utilization test [19,20,21,22,23,24]. For identification of Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus hominis, the Bruker MALDI Biotyper® IVD was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions.