Extended Data Fig. 2. Identification of B. xylanisolvens as a nicotine degrader.
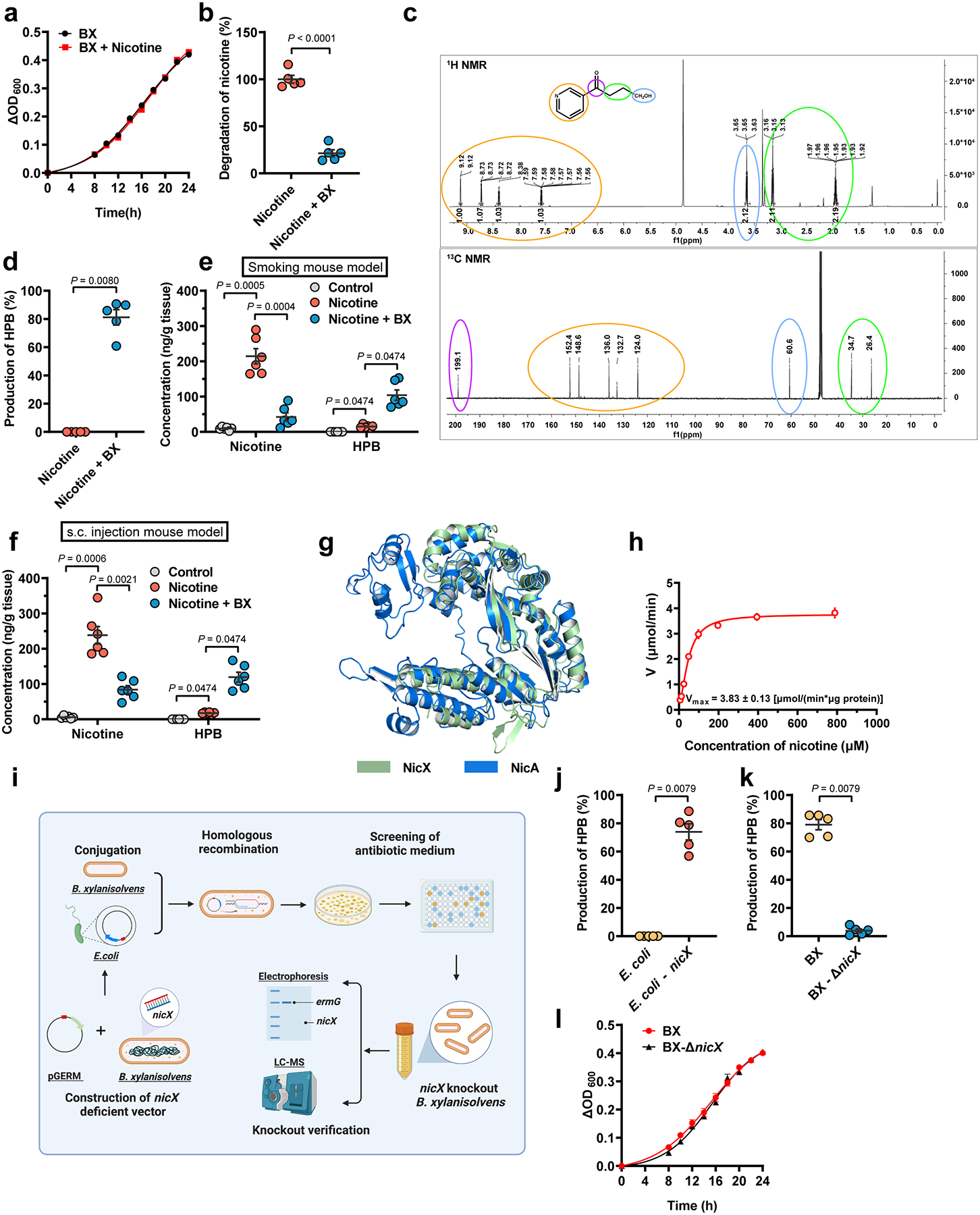
a, Growth curves of B. xylanisolvens with or without nicotine in culture medium (n = 3/group). b, Nicotine concentration in B. xylanisolvens in vitro cultivation compared with control (BHI medium with nicotine supplementation, n = 5/group). c, 1H NMR spectrum (top) and 13C NMR spectrum (bottom) of HPB. d, Production of HPB in B. xylanisolvens in vitro supplementation compared with control (BHI medium with nicotine supplementation, n = 5/group). e, Nicotine and HPB concentration in ileal tissues of smoking exposure mouse model for two weeks (SPF, n = 6 mice/group). f, Nicotine and HPB concentration in ileal tissues of subcutaneous injection mouse model for two weeks (SPF, n = 6 mice/group). g, Structural alignment of the SWISS-MODEL50-predicted B. xylanisolvens NicX and predicted Pseudomonas putida NicA. The Root-Mean-Square-Deviation (RMSD) of 242 aligned residues is 1.323 Å. h, Nonlinear regression for nicotine degradation catalyzed by purified NicX. The reaction mixture contained 1 mM FMN, 25 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.6), 20 ng NicX, and nicotine in different concentration at 37 °C, n = 3/group. i, Schematic diagram illustrating the workflow for nicX gene deletion in B. xylanisolvens. j, Production of HPB in E. coli and E. coli + nicX in vitro cultivation (LB medium with nicotine supplementation, n = 5/group). k, Production of HPB in B. xylanisolvens and B. xylanisolvens-ΔnicX in vitro cultivation in culture medium (BHI medium with nicotine supplementation, n = 5/group). l, Growth curves of WT and nicX-KO B. xylanisolvens. (n = 3/group). Data are the means ± s.e.m. a, b, l, Two-tailed Student’s t-test. d, j, k, Two-tailed Mann-Whitney U-test. e, f, for Nicotine, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s T3 post hoc test; for HPB, Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s test. Experiments in a, b, d, h, j, k, l were performed three times independently.
