Figure 1: Disrupting the mPFC with DREADDs impaired off-line hippocampal SWR rates.
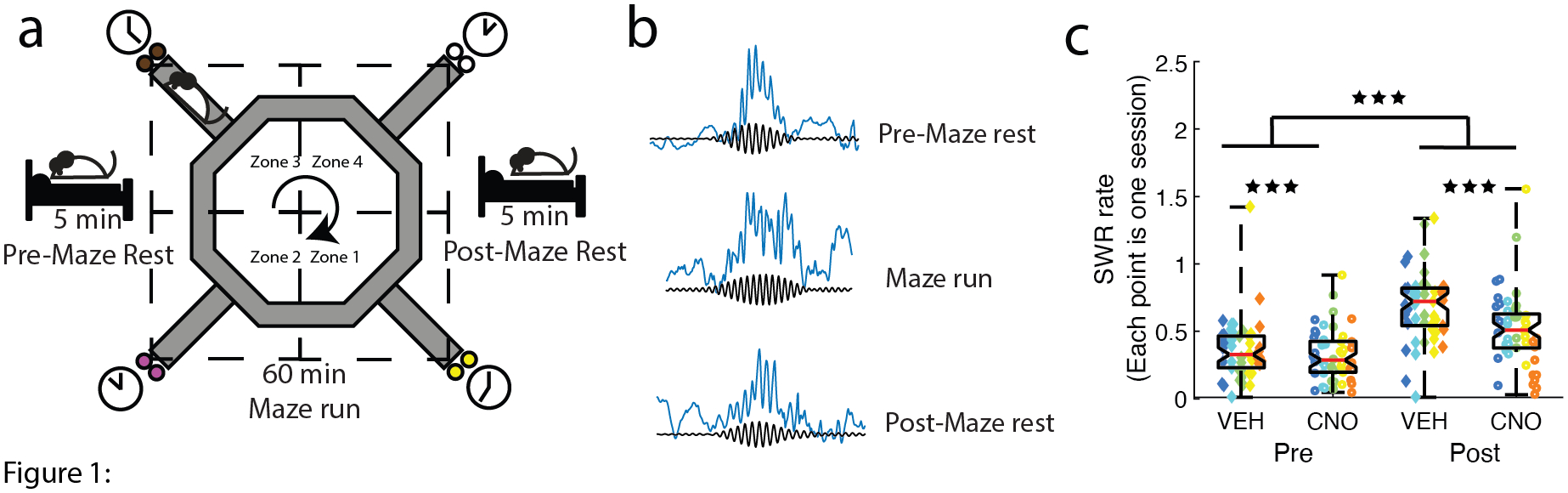
a) Schematic of the daily paradigm. On Restaurant Row, rats are required to make serial stay/skip choices for different flavored food rewards (color reflects flavor: white, plain; yellow, banana; pink, cherry; brown, chocolate). When a rat entered a restaurant/zone (demarcated by the dashed lines), a delay counted down reflecting how long the rat needed to wait to receive the food reward (1–30 sec). The rat could wait out the delay to receive the food reward or skip the current restaurant and proceed to the next. The mPFC was transfected with the inhibitory DREADDs (Schmidt et al., 2019) and rats were given daily injections of VEH or CNO before recording. b) Neuronal ensembles and local field potentials in the hippocampus were recorded during three behavioral epochs: 5-minute pre-maze record (Pre), on the maze, and 5-minute post-maze record (Post). c) SWR rates were examined on VEH and CNO days during the Pre and Post recordings. SWR rates increased from the Pre-maze to the Post-maze sessions. Disrupting the mPFC with CNO impaired this effect. Though SWR rates increased from the Pre-maze to Post-maze on CNO days, the increase in VEH Post-maze SWR rates vs. Pre-maze rates were significantly higher than on CNO days. Boxplot center mark depicts the median (red line), and top and bottom edges represent first and third quartiles. Whiskers extend to extreme data points not considered outliers. Different colors represent different rats. Diamonds = VEH days, circles = CNO days. ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
