Figure 4: Waiting SWRs are modulated by flavor preference and value.
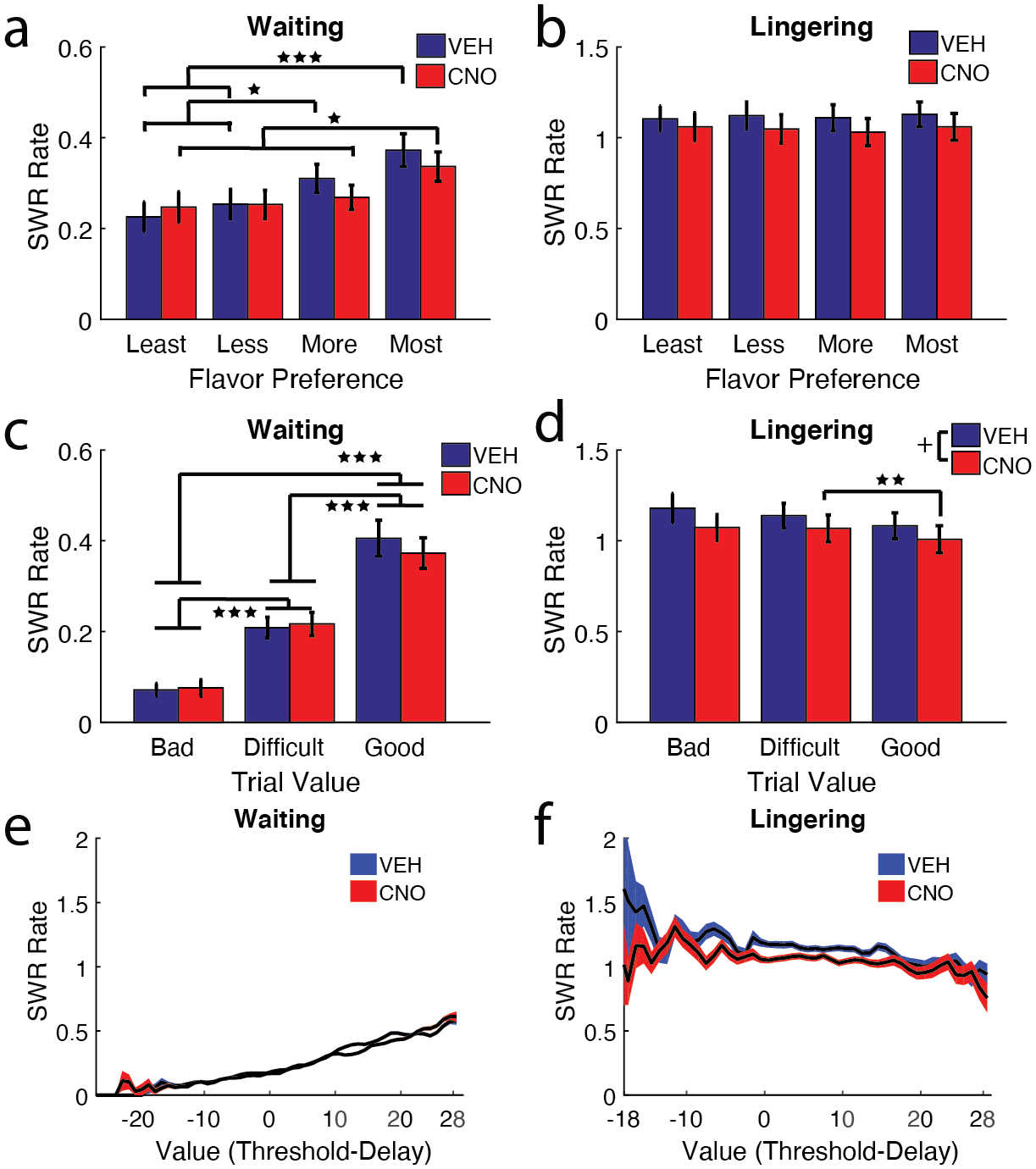
a) The four restaurants (banana, chocolate, plain, and cherry) were ranked for each rat in order of flavor preference (Most = 1st, More = 2nd, Less = 3rd, Least = 4th). SWR rates tracked with flavor preferences on the VEH Waiting epoch, higher for the most preferred flavors and lower for the least preferred flavors (Most > Less & Least***; More > Less & Least*). This relationship was disrupted on the most preferred restaurants on CNO days (Most > More & Least *). b) Lingering SWR rates didn’t track with flavor preference, SWR rates were mostly uniform across flavors. c) Individual trials were designated a Good Value (delay lower than threshold), Difficult Decision (close enough to threshold that it’s not obvious if they should take the deal), or a Bad Value (delay higher than threshold). Waiting epoch SWR rates were linearly correlated with trial value (VEH/CNO: Bad Deals < Difficult & Good***, Difficult < Good***). d) Lingering SWR rates, in contrast, did not show an effect of Trial Value, though CNO SWR rates were lower on Good deals than Difficult deals. e) Measuring Waiting SWR rates across the spectrum of trial values showed a positive linear relationship, SWR rates increased as trial value increased. f) Measuring Lingering SWR rates across the spectrum of trial values revealed a small negative correlation. + p = 0.0507, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
