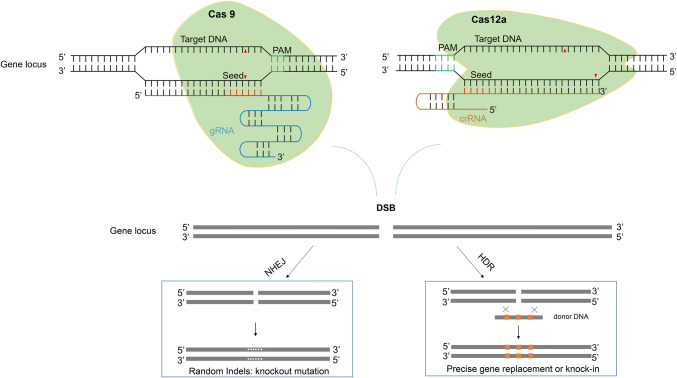
Fig. 1.
Two major pathways underlying the repair of DSB induced by CRISPR/Cas. There are two major pathways underlying the repair of double-stranded break (DSB) induced by CRISPR/Cas (Cas9 or Cas12a). One is a error-prone non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway, which generally generates random indels for knock-out mutagenesis. Another one is homology-directed repair (HDR), which is a precise repair pathway and is generally used for targeted gene/allele replacement or knock-in