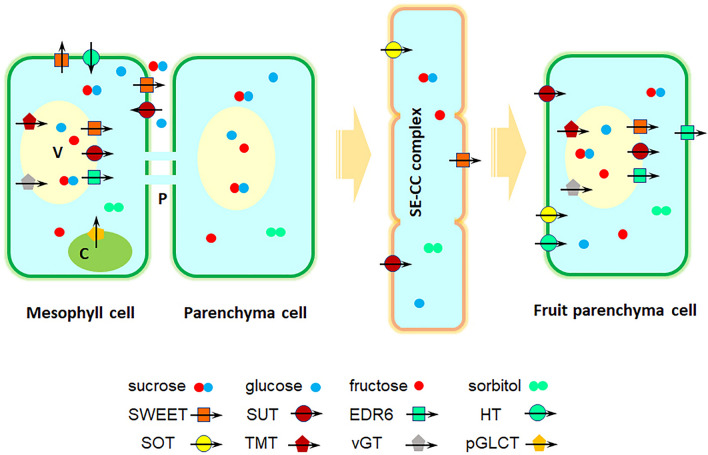
Fig. 2.
Sugar transport from leaves to fruit in apple. Sorbitol and sucrose are loaded into phloem and then unloaded into fruit parenchyma cells (Ruan et al. 2014; Wei et al. 2014). In apples, sorbitol transporters (SOTs), sucrose transporters (SUTs), SWEETs, monosaccharide transporters (MSTs) [including hexose transporters (HTs), tonoplast membrane transporters (TMTs), vacuolar glucose transporters (vGTs), ERD six-like transporters (EDR6), and plastid glucose transporters (pGLCT)] are major enzymes involved in sugar transport. SWEETs are uniporters mainly mediating the export of sugars. SUTs, SOTs, and HTs are H+/sugar importers importing Sor, Suc, and hexose. vGTs and TMTs function as sugar/H+ antiporters mobilizing sugars into vacuoles, while EDR6 and SWEET IV subfamilies are involved in sugar efflux from vacuoles. In addition, pGLCTs modulate sugar efflux from plastids. Note: C chloroplasts, P plasmodesmata, SE-CC complex sieve element/companion cell complex, V vacuoles