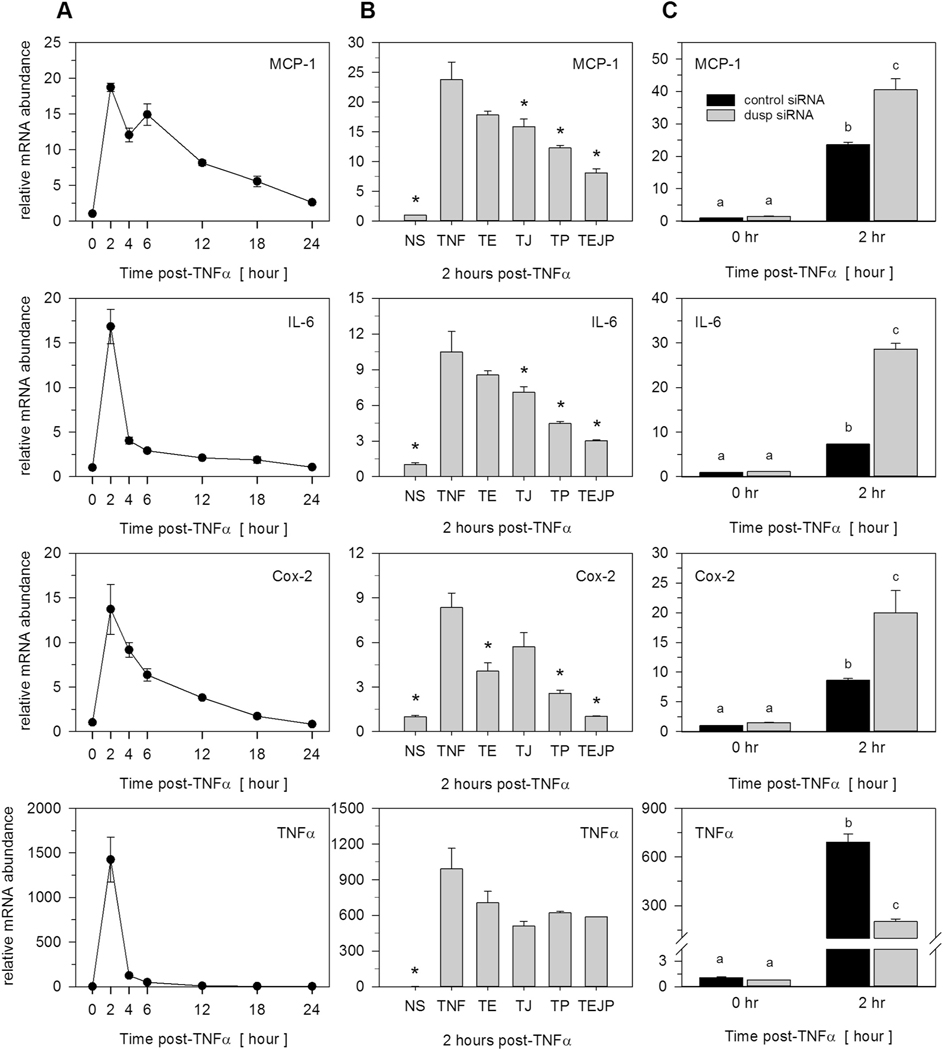
Fig. 7.
TNFα-induced MAPK-dependent and MAPK-independent proinflammatory gene expression. (A) Total RNA was harvested over time from preadipocytes stimulated with 100 pM TNFα. Proinflammatory gene expression of MCP-1, IL-6, Cox-2, and TNFα was examined by qRT-PCR. Genes were selected as ‘inducible’ when upregulated above a 2-fold criterion. (B) Preadipocytes were pretreated (1 h) in the presence of inhibitors for ERK (U0126, 10 μM), JNK (SP600125, 20 μM), or p38 (SB203850, 10 μM) prior to TNFα stimulation. Total RNA was harvested 2 h post-TNFα stimulation and mRNA expression assessed by qRT-PCR. Nomenclature assigned as: T (TNFα), T + E (TNFα+ERK inhibitor), T + J (TNFα+JNK inhibitor), T + P (TNFα+p38 inhibitor), or TEJP (TNFα+ERK + JNK + p38 inhibitors). Data were expressed relative to unstimulated cells and normalized to the 18S rRNA. Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc analysis conducted to assess differences from TNFα when p < 0.05. (C) Preadipocytes were transfected for 72 h with non-targeting control siRNA or combined pools of siRNAs for Dusp1, Dusp8, and Dusp16 prior to TNFα (100 pM) stimulation. Total RNA was collected at 0 h or 2 h post-TNFα stimulation and qRT-PCR used to examine MCP-1, IL-6, Cox-2, and TNFα. Significant differences were determined by ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc analysis performed when the p value for the respective parameter was statistically significant (p < 0.05).