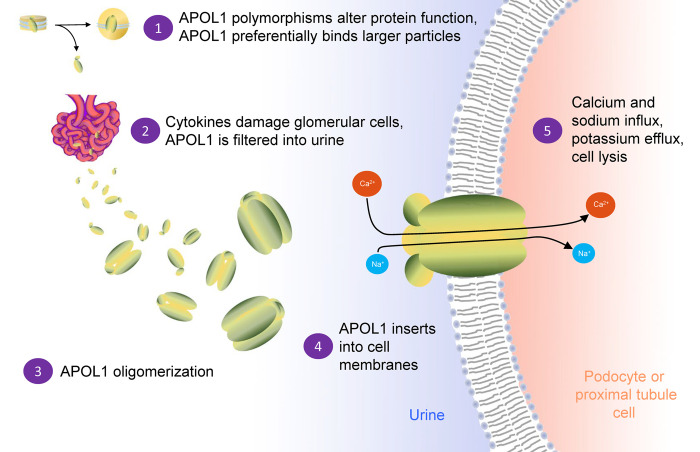
Fig 6. A speculative model for the role of circulating APOL1 in kidney injury.
High-risk coding variants have different biochemical characteristics in plasma compared with APOL1-G0 and are associated with larger particles. Leakage of APOL1 into Bowman’s space in a manner similar to albumin allows for the formation of APOL1 multimers that can insert into the plasma membrane of podocytes or proximal tubule cells once the pH of the glomerular filtrate becomes acidic. Calcium and sodium influx and subsequent potassium efflux leads to proximal tubule cell death and exacerbated kidney injury.