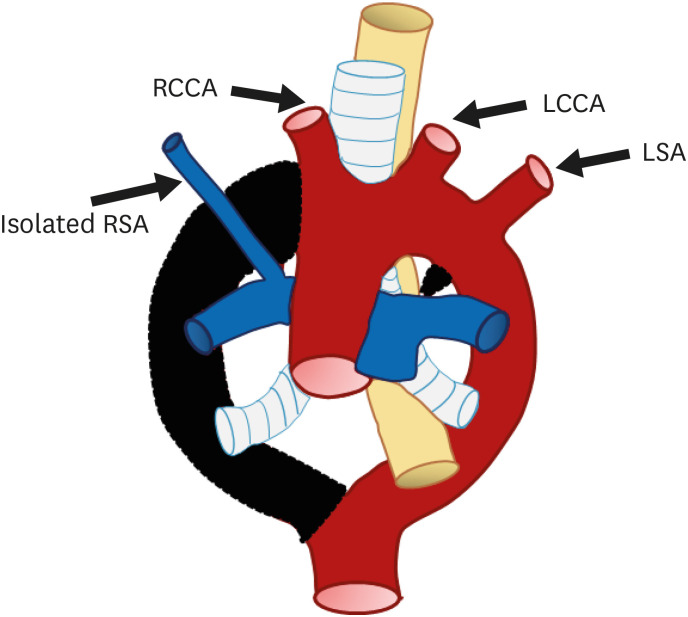
Figure 10. Schematic figure of the left aortic arch with an isolated right subclavian artery. Black-shaded area represents involuted segments in a hypothetical double arch. This anomaly results from (i) regression of the right arch between the origin of the right common carotid artery and right subclavian artery and (ii) distal to the origin of the right ductus and right subclavian artery. Thus, the right subclavian artery is connected to the pulmonary artery instead of the aortic arch.
LCCA: left common carotid artery, LSA: left subclavian artery, RCCA: right common carotid artery, RSA: right subclavian artery.