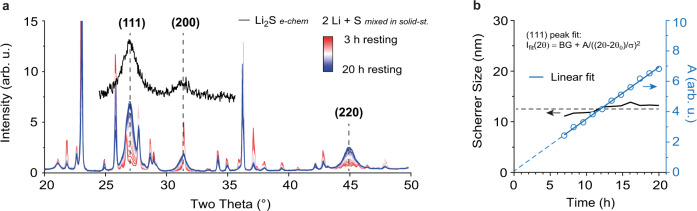
Fig. 5. Evaluation of the Li2S formation via solid-state conversion.
a X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of solid Li mixed with solid S (in a molar ratio of 2:1) after different resting times at 25 °C ± 3 °C (red to blue solid lines). While the sharp S diffraction peaks decreased, broader Li2S diffraction peaks evolved. The Li2S peaks show a similar width as the Li2S obtained from electrochemical discharge (black solid line). b The Scherrer crystallite size of the (111) peak is 7 nm for Li2S obtained from electrochemical discharge and around 12.5 nm for Li2S obtained by mixing solid S and Li. With increasing resting time, the Li2S diffraction peaks grow, their width and the crystallite size remain constant. This is shown based on a Lorentzian peak fit of the form .