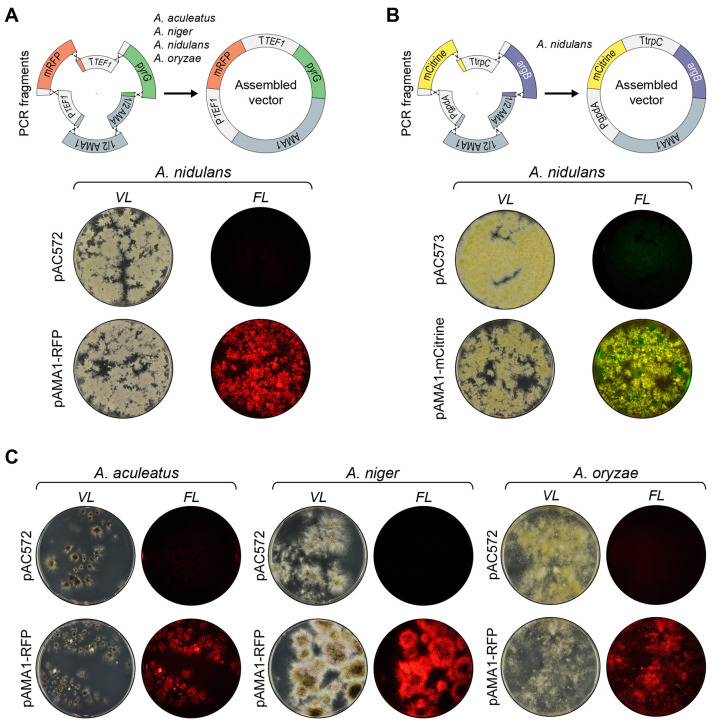
Figure 2.
E. coli sequence-free (ESF) plasmid construction by in vivo DNA assembly. (A) Top, strategy for the assembly of a fungal pAMA1-mRFP plasmid devoid of E. coli sequences. Six PCR fragments are joined by in vivo DNA assembly via 50 bp overhangs: TEF1 promoter, mRFP open reading frame, TEF1 terminator, pyrG selectable marker, and two overlapping AMA1 fragments as indicted. Matching fusion sequences are indicated by identical colors. The plasmid parts are not drawn to scale. Below, transformation of the NHEJ deficient A. nidulans strain NID2695 with pAC572, an AMA1-pyrG control vector, or with the six PCR fragments required for construction of pAMA1-mRFP by in vivo DNA assembly as indicated. Transformation plates were imaged at visible light (left) and in a setup detecting red fluorescence (right). (B) Top, strategy for the assembly of the fungal ESF plasmid pAMA1-mCitrine. Six PCR fragments are joined by in vivo DNA assembly via 50 bp overhangs: gpdA promoter, mCitrine open reading frame, trpC terminator, argB selectable marker, and the two overlapping AMA1 fragments. Below, transformation of the NHEJ deficient A. nidulans strain NID2695 with pAC573, an AMA1-argB control vector, or with the six PCR fragments required for construction of pAMA1-mCitrine by in vivo DNA assembly as indicated. Transformation plates were imaged at visible light (left) and in a setup detecting yellow fluorescence (right). (C) Transformation of NHEJ deficient strains of A. aculeatus, A. niger, and A. oryzae with a AMA1-pyrG control vector (pAC572) or with the six PCR fragments required for the construction of the ESF plasmid AMA1-mRFP by in vivo DNA assembly. Transformation plates for each species are shown in individual panels as indicated. For each panel, plates representing transformation with pAC572 and with the six PCR fragments required for construction of the plasmid AMA1-mRFP are shown in the top and bottom, respectively. In all panels, plates were imaged at visible light (left) and in a setup detecting red fluorescence (right).