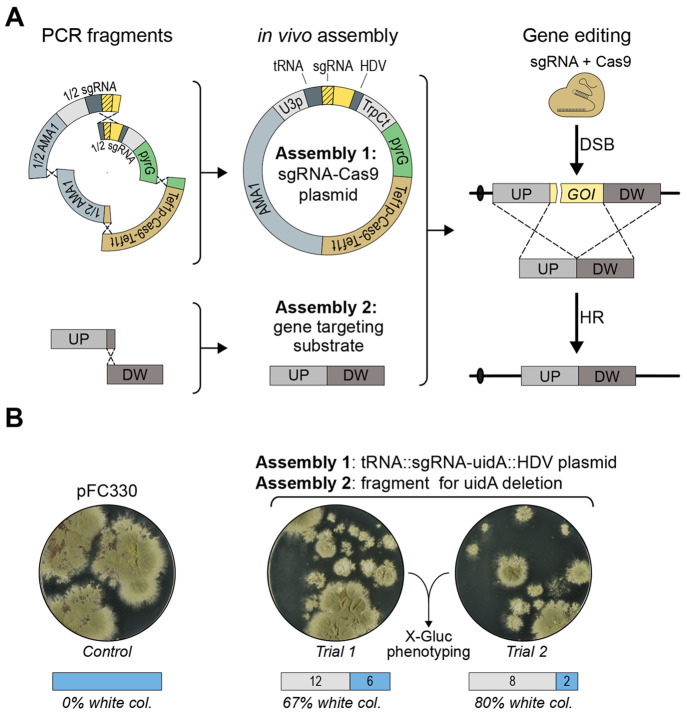
Figure 5.
Cloning- and marker-free gene deletion. (A) An ESF-CRISPR vector containing a unique sgRNA expression cassette and a marker-free gene-targeting substrate for gene deletion are constructed in parallel in two independent in vivo DNA assembly reactions. The ESF-CRISPR vector is assembled from four different PCR fragments. Importantly, two of the PCR fragments are fused via tags that include the variable moiety of the sgRNA sequence to produce the unique sgRNA expression cassette. Since the fusion tags are included in the primer tails, the coding sequence of the sgRNA gene can be easily reprogrammed to match new target sites. The marker-free gene deletion substrate is formed by fusing two PCR fragments containing up- and downstream sequences of the target gene. After in vivo DNA assembly of the two constructs, Cas9 introduces a specific DNA DSB in the target gene, and repair of this break using the gene-targeting substrate produces the desired deletion. (B) Transformation of NID1 with pFC330 (left), and with the two PCR fragments required for the assembly of the gene-targeting substrate for deletion of uidA and the four fragments required to build the uidA ESF-CRISPR vector (right).