FIGURE 3.
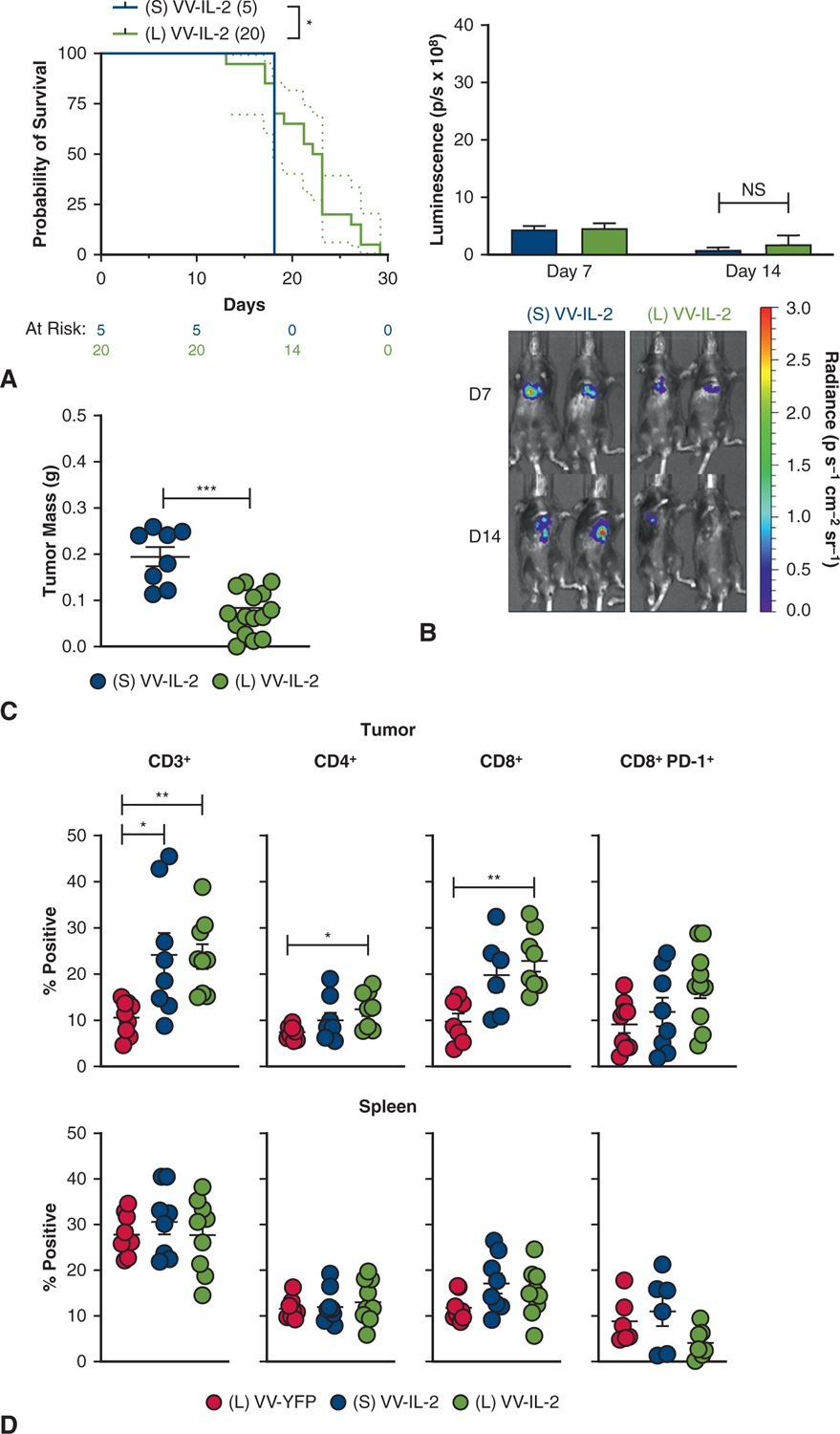
Intrapleural IL-2 expressing VV demonstrates superior antitumor efficacy compared with systemic (intraperitoneal) administration. A, Kaplan–Meier survival estimate (with 95% confidence interval) for MPD mice treated with systemic VV-IL-2 (n = 5) or intrapleural VV-IL-2 (n = 20) at 2 × 108 pfu per mouse 7 days post-tumor inoculation (2 pooled experiments) demonstrates survival benefit with intrapleural VV-IL-2 treatment. B, There was no difference in tumor bioluminescence (photons/s × 108) between systemic and local VV-IL-2 in bioluminescence (3 separate experiments). C, Intrapleural VV-IL-2 resulted in less tumor burden (2 pooled experiments). D, Flow cytometry analysis of CD3+, CD4+ CD8+, and CD8+ PD-1+ (percent of all live cells) immune populations showed elevated intratumoral CD3+ both systemic and local VV-IL-2, but only increased CD4+ and CD8+ infiltrate after intrapleural VV-IL-2 versus VV-YFP control (3 separate experiments). The same immune populations were not altered in the spleen. P values are reported (*P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001).
