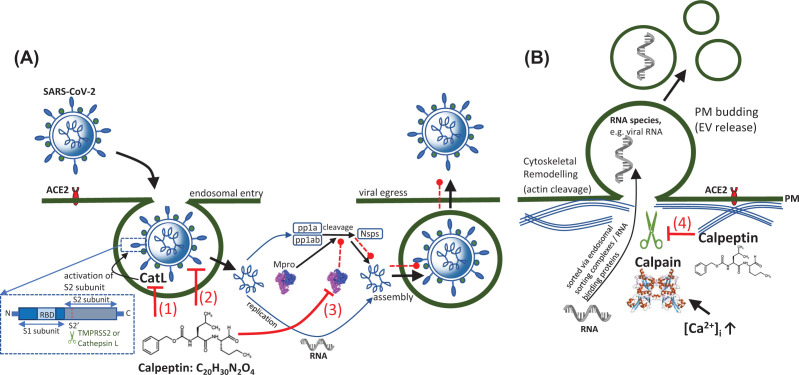
Figure 1. Calpeptin-mediated inhibition of calpain and its effect on SARS-CoV-2 entry and egress.
(A) During SARS-CoV-2 endosomal entry, in TMPRSS- or low expressing cells, SARS-CoV-2 follows a slow, pH-dependent pathway. Here, calpeptin inhibits cathepsin L- (CatL-) mediated activation of the S2 subunit of the S protein, thereby blocking viral entry (1). Calpeptin can also block viral entry by high-affinity binding to the S protein RBD thereby blocking S protein: ACE2 interaction (2). Calpeptin binds with high affinity to Mpro thereby preventing cleavage of polyproteins pp1a and pp1ab into the nonstructural proteins 1–16, resulting in inhibition of assembly and viral egress (3). In (B), calpeptin inhibits calpain-mediated remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton, thereby inhibiting the release of shedding EVs which may incorporate various viral macromolecules (4). Any such regulation of EV release may help reduce EV-mediated fibroblast proliferation and pulmonary fibrosis.