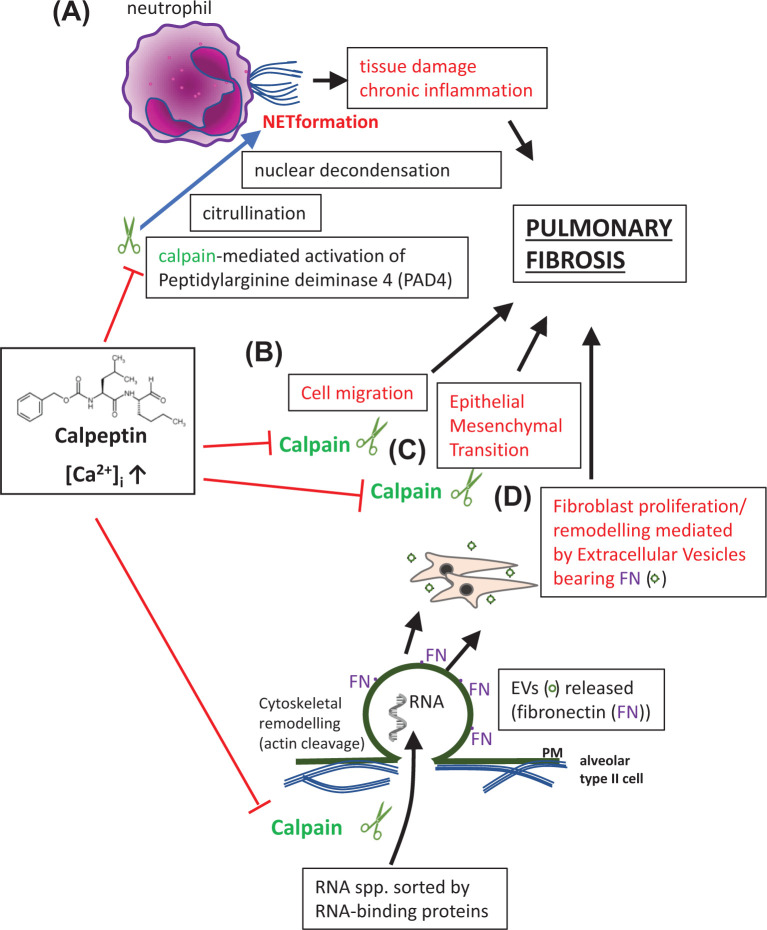
Figure 2. Calpeptin-mediated inhibition of calpain reduces inflammation and PF in COVID-19.
(A) Calpleptin inhibits calpain activation of PAD4 and in turn citrullination, nuclear decondensation and NETosis-mediated tissue damage, inflammation and lung fibrosis. (B) Calpeptin inhibits calpain-mediated inflammatory cell migration and (C) EMT-mediated lung fibrosis, both leading to lung fibrosis. In (D), calpeptin inhibits calpain-mediated plasma membrane budding and fibroblast remodeling due to the FN bearing EVs.