Figure 1.
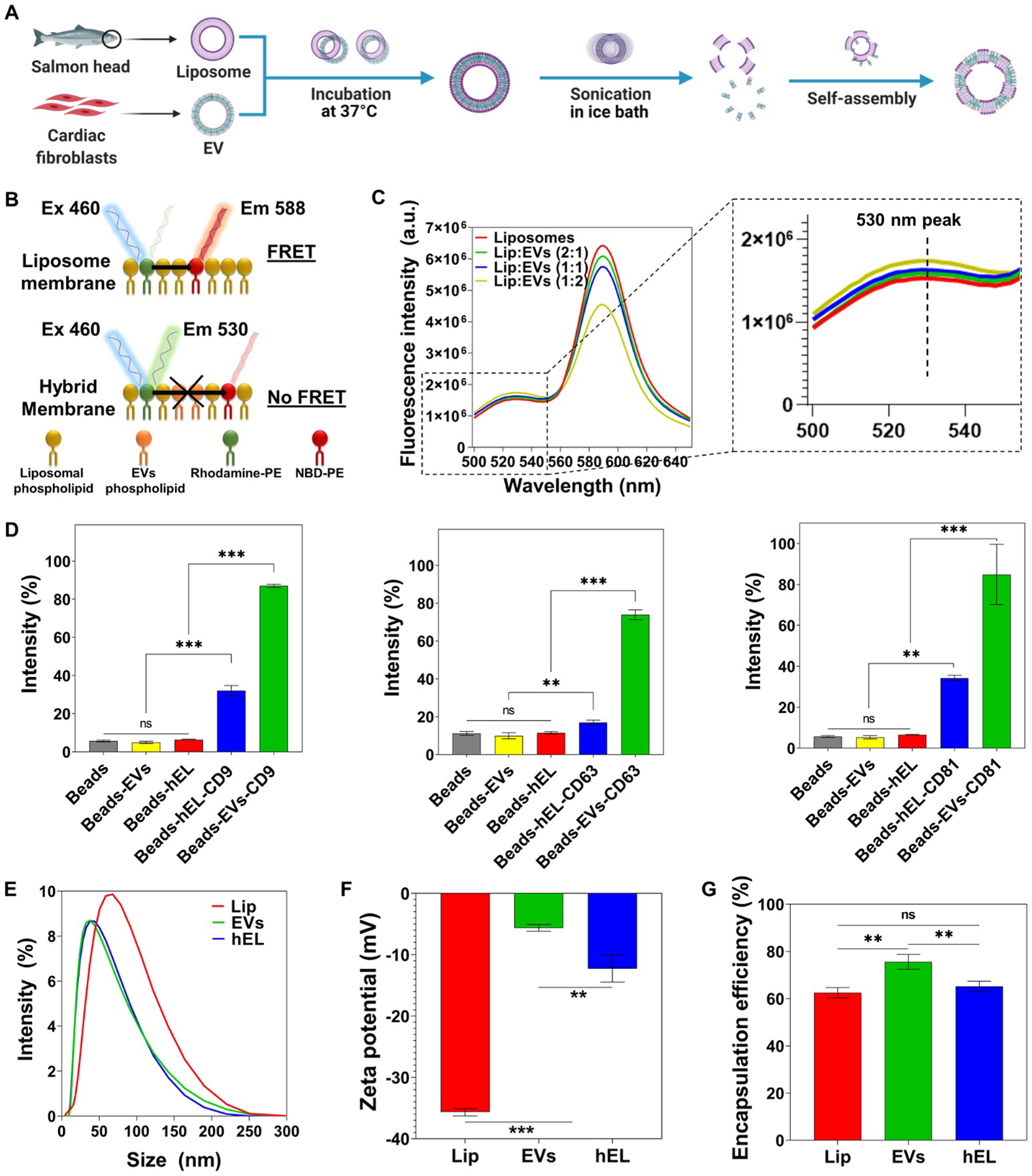
Fabrication and characterization of Lip, EVs, and hybrid (hELs) nanovesicles (NVs). (A) Schematic of the synthesis procedure of hELs NVs. Created with BioRender.com. (B) Schematic of the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) analysis assay used to monitor the fusion between EVs and Lip. (C) FRET assays were performed for various ratios of Lip to EVs (1:0, 2:1, 1:1, and 1:2) with excitation at 460 nm. (D) Expression of CD9, CD63, and CD81 markers on EVs and hELs was analyzed by flow cytometry (n=3). (E) Size distribution of NVs was measured by DLS. (F) Average zeta-potential of NVs (n=3). (G) Encapsulation efficiency of miRNA-DY547 by NVs (n=3). All data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Significance is indicated as **(p < 0.01) and ***(p < 0.001).
