Figure 1.
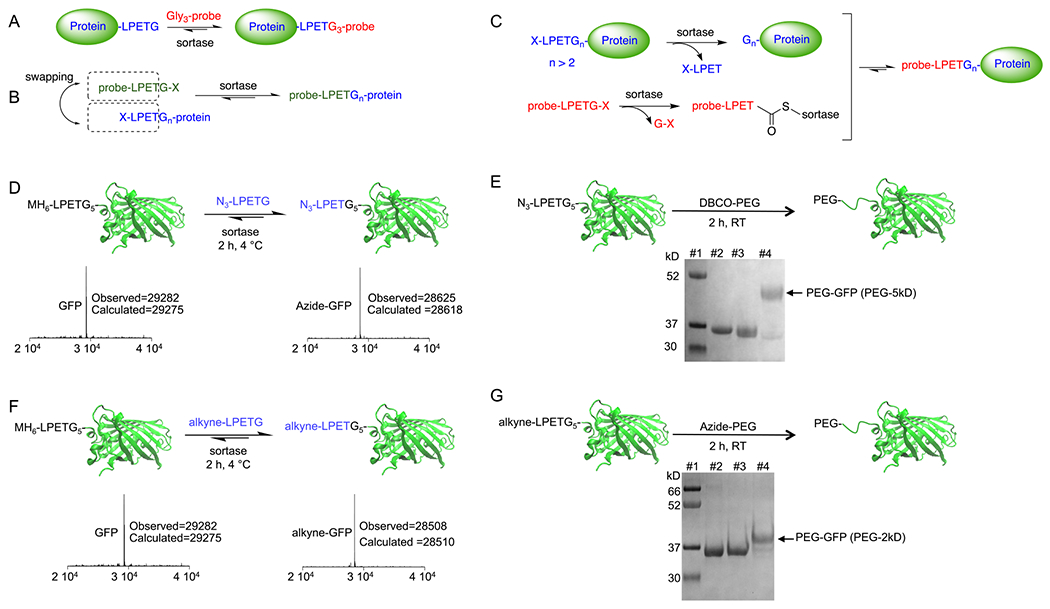
Site-specific N-terminal labeling using the sortase-mediated swapping approach. (A) Traditional sortase reaction for site-specific C-terminal protein labeling. (B) Schematic representation of the direct N-terminal protein labeling using the sortase-swapping approach. (C) The hypothesized mechanism for the direct N-terminal protein labeling. (D) GFP was directly labeled at its N terminus using an azide-functionalized LPETG-containing substrate; LC-MS analyses confirmed the formation of the product. (E) The N-terminally installed click handle can be used to site-specifically attach different molecules to the protein, such as a PEG moiety; SDS-PAGE analysis was used to confirm the formation of PEGylated GFP. Lanes #1: marker, #2: MH6LPETGGGGG-GFP, #3: azide-functionalized GFP, #4: PEGylated-GFP (5 kDa PEG). (F) GFP was directly labeled at its N terminus using an alkyne-functionalized LPETG-containing substrate; LC-MS analyses confirmed the formation of the product. (G) The N-terminally installed alkyne click handle can be used to site-specifically attach different molecules to the protein, such as a PEG moiety; SDS-PAGE analysis was used to confirm the formation of products. Lanes #1: marker, #2: MH6-LPETGGGGG-GFP, #3: alkyne-functionalized GFP, #4: PEGylated-GFP (2 kDa PEG).
