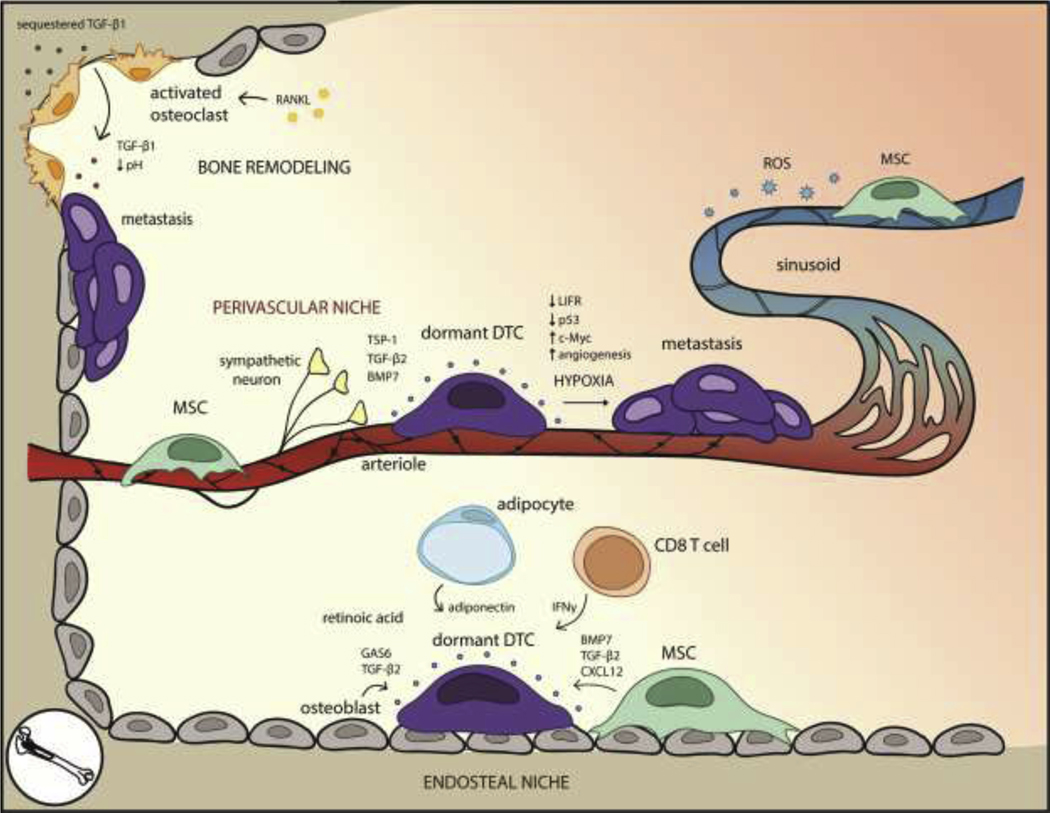
Figure 1. The bone microenvironment for dormant DTCs is well-defined due to established mechanisms that regulate HSC quiescence and bone resorption.
Within the endosteal niche, MSCs, osteoblasts, adipocytes, and CD8+ T cells secrete factors that preserve DTC quiescence. High levels of retinoic acid within the bone marrow induce cell cycle arrest. Awakening can occur as the result of environmental changes brought on by RANKL-activated osteoclasts and bone resorption. In the perivascular niche, arterioles and perivascular cells promote DTC quiescence through basement membrane factors such as TSP-1, although hypoxic regions near the vessels promote angiogenesis, which correlates with metastasis. The leakier sinusoids, by contrast, experience ROS on the basal side of the vessel, possibly inducing DNA damage and stress pathways associated with metastasis.