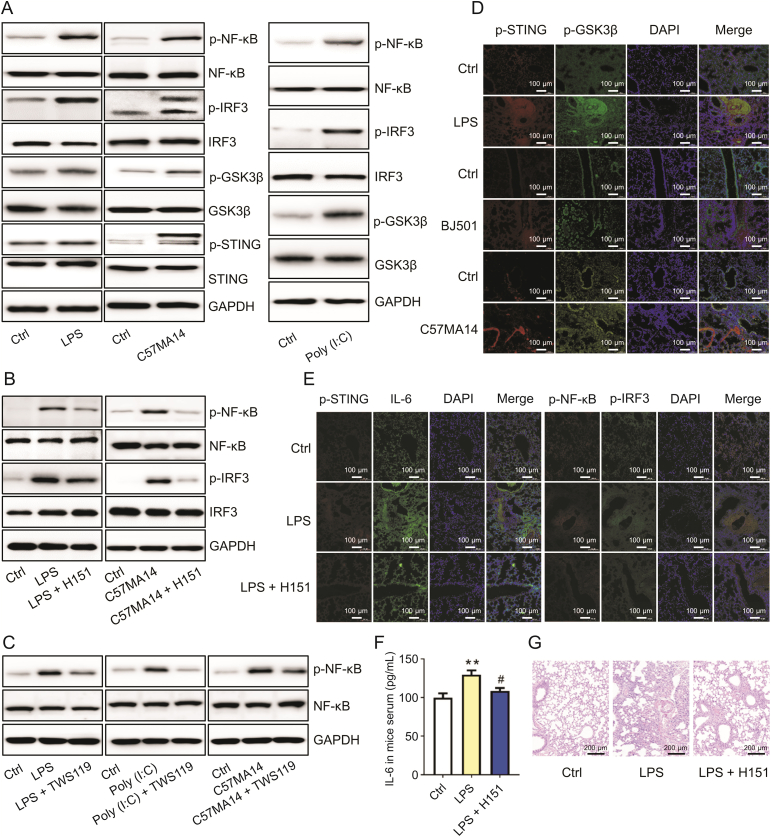
Fig. 3.
Infection activated stimulator of interferon genes (STING) and glycogen synthase kinase-3-beta (GSK3β) signaling. (A) After 10 ng/mL lipopolysaccharide (LPS), C57MA14 (MOI = 0.1), or 50 μg/mL Poly (I:C) infection for 24 h, RAW264.7 cells were collected and lysed with specified antibodies for Western blot (n = 3). (B, C) RAW264.7 cells were subjected to LPS or Poly (I:C) and treated with 10 μM H151 (B) or 10 μM TWS119 (C) for 24 h. NF-κB and IRF3 phosphorylation levels were measured by immunoblot (n = 3). (D) Mice were challenged with 5 mg/kg LPS, 0.1∗LD50 Beijing/501/2009 strain (BJ501), or 0.1∗LD50 C57MA14. Lung tissue sections were stained with p-STING (red) and p-GSK3β (green) antibodies. Nuclei were stained with 40,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue) (n = 5). (E) Mice were stimulated with LPS and treated with 7 mg/kg H151 for 24 h. Lung tissue sections were subjected to immunofluorescence assay with p-STING (red), IL-6 (green), p-IRF3 (green), and p-NF-κB (red) antibodies. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue) (n = 5). (F) Mice were treated as described in (D). Serum IL-6 in serum was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (n = 5). (G) Mice were treated as described in (D). Lung tissue sections were subjected to hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining (n = 5). p-GSK3β: anti-phospho-GSK3β; p-STING: anti-phospho-STING; p-IRF3: anti-phospho-IRF3, p-NF-κB: anti-phospho-NF-κB; DAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. ∗∗P < 0.01 vs. control. #P < 0.05 vs. LPS group.