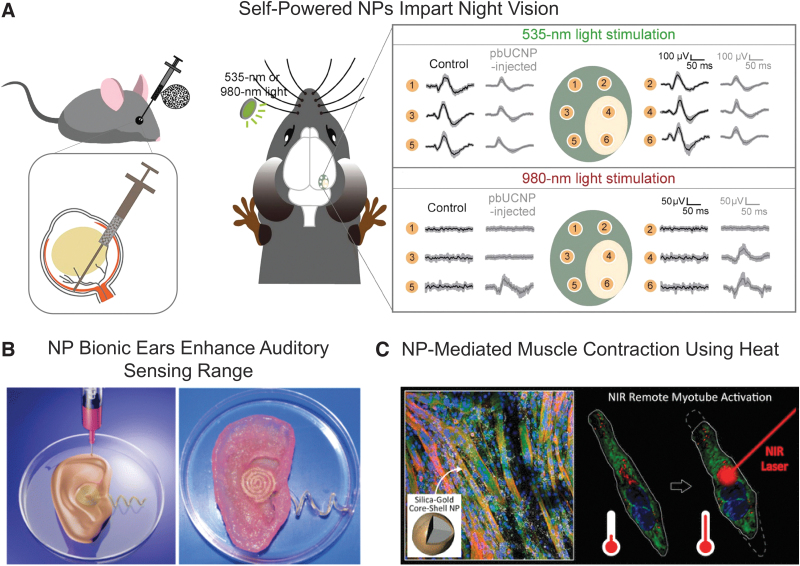
Figure 2.
Nanomaterial studies that have enhanced physiological performance. (A) An engineered nanoparticle (pbUCNP) that imparts night vision in mice. Representation of pbUCNP injection into the eye, where it binds with photoreceptor cells in the retina. pbUCNP serves as a self-powered antenna that can be stimulated at 535 nm (day vision) and 980 nm (night vision). Reprinted with permission from Ma Y.150 (B) A 3D printed bionic ear composed of a hydrogel laden with cells and conductive nanoparticles coupled to electrodes for auditory sensing. The bionic ear demonstrated enhanced auditory sensing when compared with human hearing. Reprinted with permission from the American Chemical Society.152 (C) In vitro study with muscle cells doped with gold nanoshells (ie, NPs consisting of silica coated with a thin layer of gold), where the NPs induced muscle contraction with an externally applied heat source. Reprinted with permission from the American Chemical Society.156 Abbreviations: NP, nanoparticle; pbUCNP, photoreceptor-binding upconversion nanoparticle.