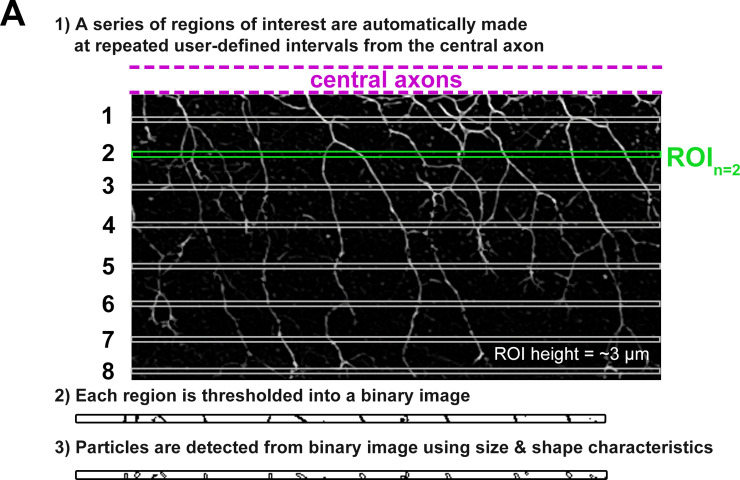
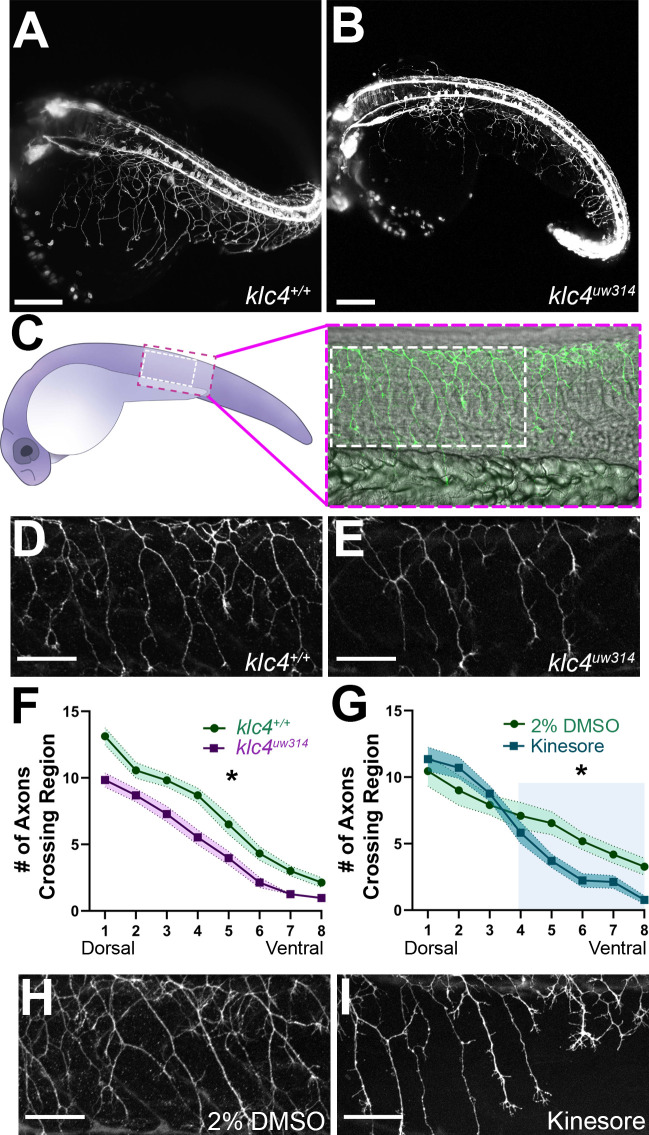
Figure 2. klc4uw314 mutants have reduced Rohon-Beard peripheral axon branching.
(A–B) Stills taken at approximately 24 hpf from long term light sheet movies of wild type (A) or klc4uw314 mutant (B) embryo development Scale bar = 150µm. (C) Diagram of a 24 hpf embryo indicating the area over the yolk tube extension imaged for axon analysis, with the standard region used for analysis outlined by the white dashed rectangle. (D–E) Representative examples of HNK-1 stained embryos showing peripheral axon branching in wild type (D) and klc4uw314 I embryos. (F–G) Quantification of axon branching across three technical replicates in wild type (n=32) and klc4uw314 mutant (n=32) embryos (F) and DMSO (n=12) and kinesore (n=17) treated embryos (G). Error bars = SEM. Statistical significance was measured by comparing the area under the curve for (F–G) using t-test. For (F), *p=0.0378 for entire graph. For (G), *p=0.0484 for shaded region. (H–I) Representative examples of HNK-1 stained embryos showing peripheral axon branching in DMSO (H) and kinesore treated (I) embryos. Scale bars for D,E,H,I = 50 µm.