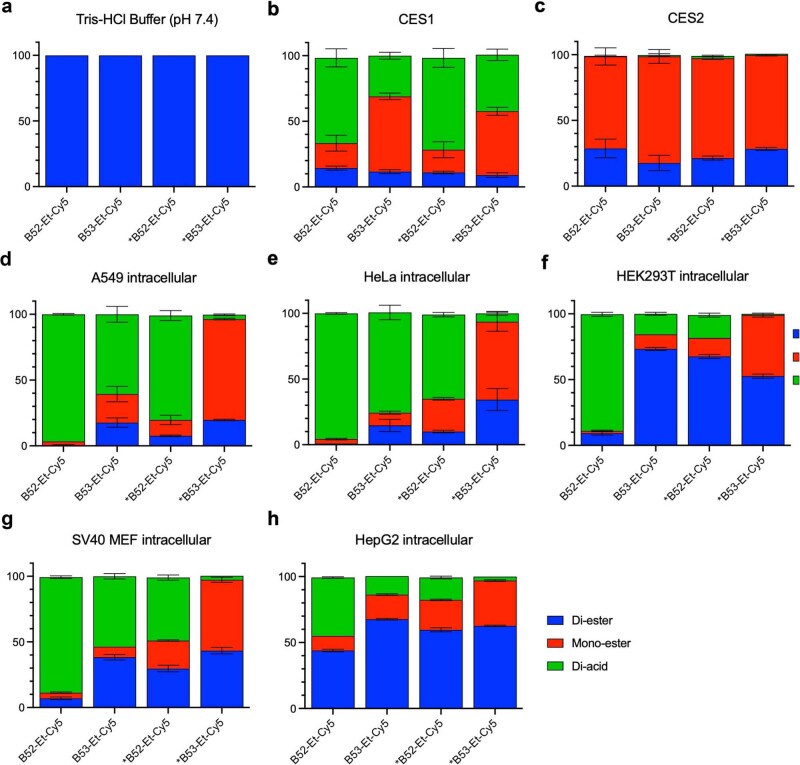
Extended Data Fig. 9. Hydrolysis of ester prodrug CypD inhibitors.
Compounds were evaluated for their ability to be hydrolyzed from di-ester to mono-ester, or to di-acid CypD inhibitors. Each reaction was analyzed by LC-MS, and ion abundances for each are shown as a percent of the total sum. These were conducted under conditions of: a, Tris-HCl buffer only; b, 250 nM carboxylesterase 1 (CES1); c, 250 nM carboxylesterase 2 (CES2); d, incubated with A549 cells for 48 h and intracellular fraction isolated; e, incubated with HeLa cells for 48 h and intracellular fraction isolated; f, incubated with HEK293T cells for 48 h and intracellular fraction isolated; g, incubated with MEFs for 48 h and intracellular fraction isolated; h, incubated with HepG2 cells for 36 h and intracellular fraction isolated. Esters show good stability in buffer and are only cleaved under esterase conditions, or intracellularly, with B52-Et-Cy5 showing the most rapidly hydrolyzed esters. Values and error bars reflect mean ± s.d. of three technical replicates.