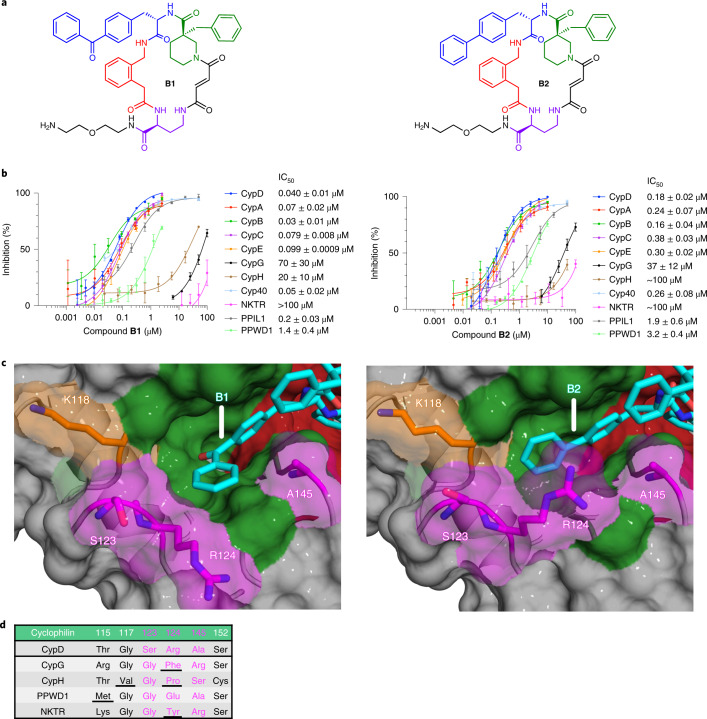
Fig. 2. Compounds with large S2 pocket binding groups show reduced potency against cyclophilins with sterically occluded S2 pockets.
a, Structure of B1, B2. b, Cyclophilin prolyl-isomerase inhibition screens for B1 and B2. c, Co-crystal structures of B1 (PDB ID 7TGU, 1.21 Å resolution) or B2 (PDB ID 7TGV, 1.46 Å resolution) bound to CypD, viewing the S2 pocket. Active site binding is identical to that of A26 (Fig. 1e). d, Residues within the S2 pocket of cyclophilins inhibited less potently by B1 and B2, with important residues underlined. The benzophenone or biphenyl group of B1 or B2, respectively, fills the S2 pocket more completely, resulting in selectivity over cyclophilins with more sterically occluded or inflexible S2 pockets. CypD by contrast contains a relatively un-occluded S2 pocket and flexible R124 residue. IC50 values reflect mean ± s.e.m. of three technical replicates. Data points and error bars reflect mean ± s.d. of individual assays at one dose.