Figure S4.
Nanoglue and Nanobreak in SPR experiments and stripe assays, related to Figure 4
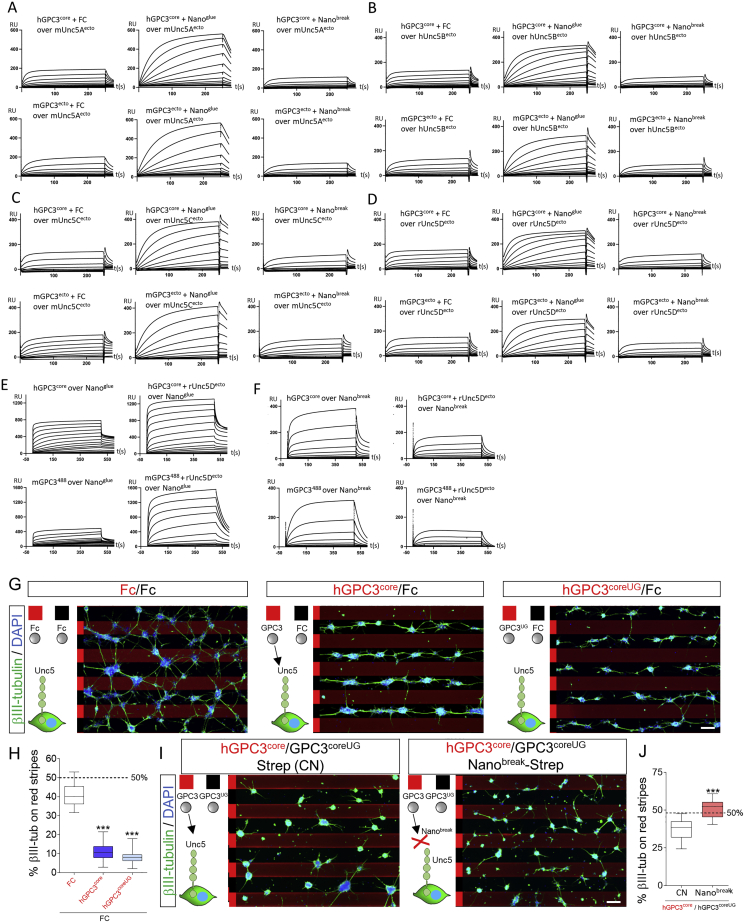
(A–D) Binding curves from SPR experiments. Unc5A-D receptor ectodomains were immobilised. Human GPC3core or murine GPC3ecto was injected using a 2-fold dilution series (top concentrations are 4.5 μM), in the presence of FC control protein, Nanoglue or Nanobreak. The concentration of nanobodies was kept constant at 9 μM (with hGPC3core), or 4.5 μM (with mGPC3ecto). The concentration of FC control protein was kept constant at equivalent mg/ml concentrations.
(E and F) An analogous experiment was performed using immobilised nanobodies, and different concentrations of human GPC3core or murine GPC3488 and Unc5Decto. Taken together, the results demonstrate that Nanobreak competes with Unc5 for GPC3-binding, whilst Nanoglue strengthens the interaction. Calculated KDs for nanobody-GPC3 interactions are shown in Figure 4C. Given the unusual stoichiometry of the Unc5-GPC3 complex, we have not calculated KD values from experiments containing also Unc5.
(G) Purified proteins were immobilised in a stripe pattern to assess their effect on the migration of cortical neurons. GPC3core and GPC3coreUG trigger strong cell repulsion, compared to neutral control protein (Fc).
(H) Quantification of the experiments shown in panel F. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc tests.∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(I) We performed GPC3core/GPC3coreUG stripe assays, but in the presence of streptavidin (CN) or streptavidin-nanobody complexes. Nanobreak reduced the ability of neurons to distinguish between hGCP3core and hGCP3coreUG.
(J) Quantification of data shown in panel H. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s T test. Scale bar represents 90 μm (G) and (I).