Figure 6.
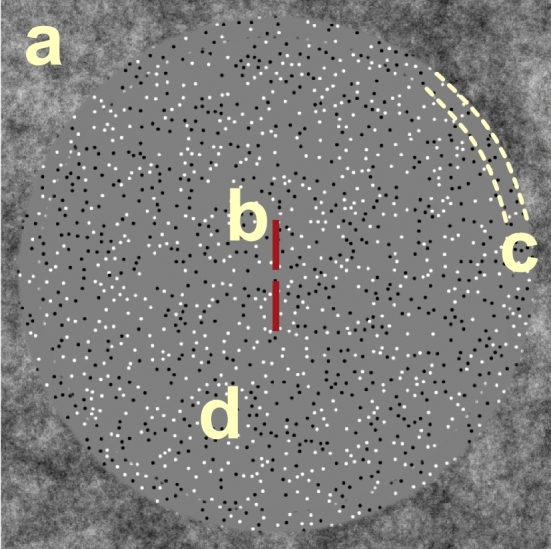
Schematic illustration of the DRDS display. A binocular, zero-disparity frame comprising 1/f noise (a) was used as a fusion lock. Dichoptic nonius lines (b) were used to engage fixation at the center of the screen and to monitor vergence. A detection task in which the color of the nonius lines changed from red to blue occurred at random intervals during both ‘attend fixation’ and ‘attend stimulus’ conditions. It was task relevant only in the ‘attend fixation’ condition. The duration of the color change was varied on a staircase which maintained an 82% detection rate. To minimize the availability of disparity references, a 1-degree gap containing binocularly uncorrelated dots (c) was interposed between the changing disparity region (d) and the fusion lock (a).
