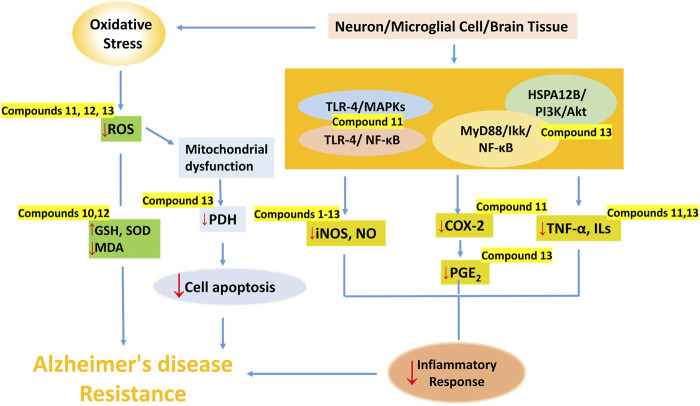
FIGURE 3.
The main mechanisms of dibenzocyclooctene lignans against AD. (Dibenzocyclooctene lignans play a protective role in the nervous system through anti-inflammation, antioxidation and inhibition of neuronal apoptosis. Compounds 1–13 inhibited the activity of NO, compounds 11 and 13 inhibited the release of downstream inflammatory factors by regulating TLR-4-mediated NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways, MyD88/IKK/NF-κB and HSPA12B/PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. In addition, Compounds 10 and 12 up-regulated the expression of SOD and GSH, and inhibited MDA in brain tissue, while compounds 11 and 13 reduced the content of ROS to resist oxidative stress. Compound 13 also inhibited apoptosis by inhibiting JNK-mediated PDH inhibition.).