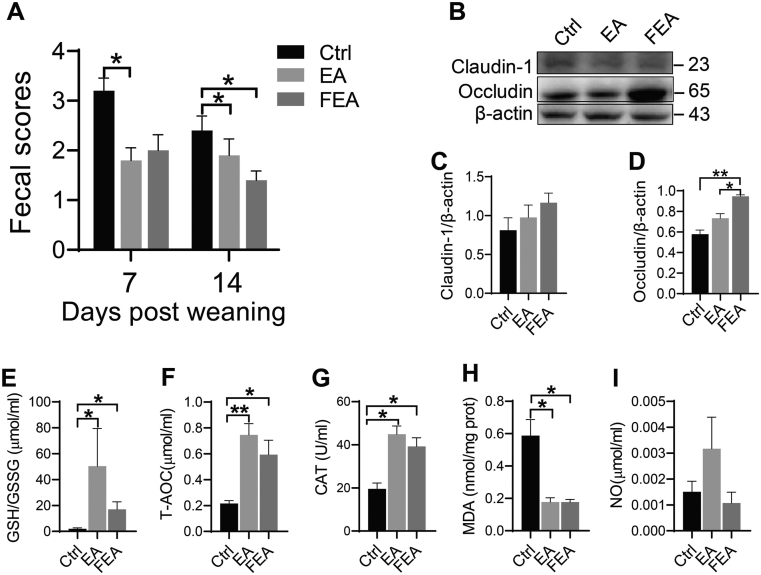
Fig. 1.
The effects of dietary ellagic acid (EA) supplementation and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) on diarrhea, intestinal damage, and redox imbalance in weanling piglets. (A) Fecal scores on d 7 and 14. (B) Representative bands for Western blot. (C and D) Western blot of tight junction proteins claudin-1 and occludin in jejunum tissue, respectively. (E-I) Antioxidant indices including GSH/GSSG, T-AOC, CAT, MDA, and NO in the jejunum tissue. Ctrl, the control group, where piglets were fed the basal diet; EA, the EA group, where piglets were fed the basal diet supplemented with EA; FEA, the FEA group, where piglets were fed the basal diet and received FMT from EA-treated piglets. GSH/GSSG = glutathione/glutathione (oxidized); T-AOC = total antioxidant capacity; CAT = catalase; MDA = malondialdehyde; NO = nitric oxide. Data presented as mean ± SEM and significance was presented as ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗P < 0.01 (n = 3).