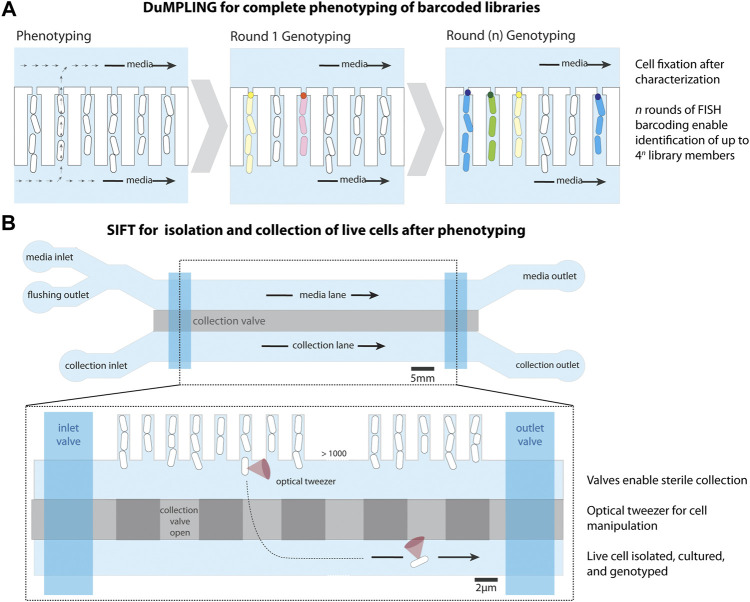
FIGURE 3.
Modifications to the mother machine to enable cell screening. (A) Dynamic u-fluidic microscopy-based phenotyping of a library before in situ genotyping” (DuMPLING), has a 300 nm gap at the end of the cell trench, allowing media to flow through the cell channels. Rounds of barcoding through FISH enable genotyping of the pooled library. Schematic representation inspired from Lawson et al. (2017). (B) Single-cell isolation following time-lapse microscopy (SIFT) uses a modified microfluidic chip containing an additional lane for cell isolation below the cell trenches, separated by a pressurized valve system (collection valve). A second set of valves (inlet and outlet) allows for the lane to be sealed for inlet cleaning and restricting media flow after cell loading. An optical tweezer moves cells of interest from their trench to a collection trap, where they are isolated and removed from the device to be cultured and sequenced. Schematic representation inspired from Luro et al. (2020).