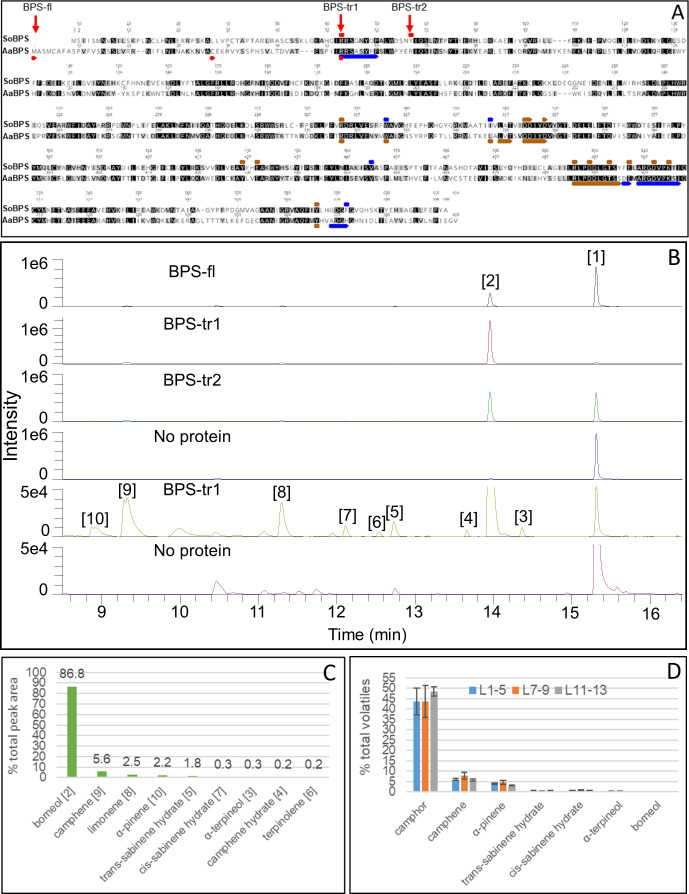
Figure 6.
Functional characterisation of AaBPS. (A) Alignment of predicted amino acid sequence of AaBPS (GenBank accession OL656813) with SoBPS (GenBank accession AF051900). Truncation points used to generate truncated versions of AaBPS are indicated as BPS-tr1 and BPS-tr2. BPS-fl represents a full length protein. Red bars – active site lid, Blue bars - active site, Brown bar – substrate binding site annotated from Whittington et al., 2002. Identical (Black) and similar (grey) positions highlighted. (B) AaBPS in vitro protein activity assay using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) based detection of monoterpenes. No protein control includes geraniol, the product of GPP hydrolysis (peak 1). Identification of peak 1 and 2 as geraniol and borneol respectively was assigned using known standards. Identities of peaks 3-10 were assigned using the NIST database and shown in (C). (C) Relative abundance of AaBPS in-vitro products for the most active truncated version of the protein (BPS-tr1). (D) Relative abundance of selected volatiles in three types of A annua Artemis leaves measured by GC-MS: L1-5 (juvenile), L7-9 (expanding), L11-13 (mature). Error bars – SE (n=6).