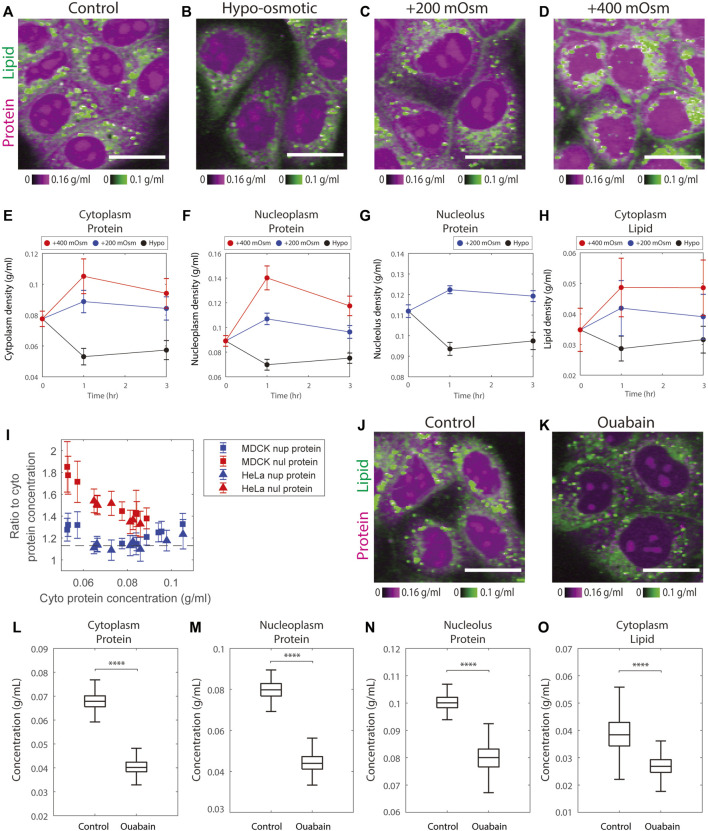
FIGURE 4.
Osmotic stress alters protein and lipid densities. (A–D) Representative NoRI images of control MDCK cells in complete medium and MDCK cells after 3 h in hypo-osmotic or hyper-osmotic media. Scale bar, 20 µm. (E–H) Time course of protein and lipid density change by hyper-osmotic and hypo-osmotic treatment. Time 0 shows the control sample. Data points and error bars are the mean and standard deviation. The number of cells in each data point is between 452 and 1204 cells, with a mean of 790 cells. (I) The ratio of nucleoplasm (nup) or nucleolus (nul) protein density to cytoplasm protein density versus cytoplasm protein density measured in the control, hypo-, and hyper-osmotic media. The dashed line indicates the mean ratio between nucleoplasm and cytoplasm protein density from Figure 2J. (J–K) Representative NoRI images of control MDCK cells and MDCK cells treated with 3 µM ouabain for 5 h. Scale bar, 20 µm. (L–O) Change of protein and lipid density in cytoplasm, nucleoplasm, and nucleolus in MDCK cells treated with 3 µM ouabain for 5 h. n = 548 (Control).n = 665 (Ouabain).