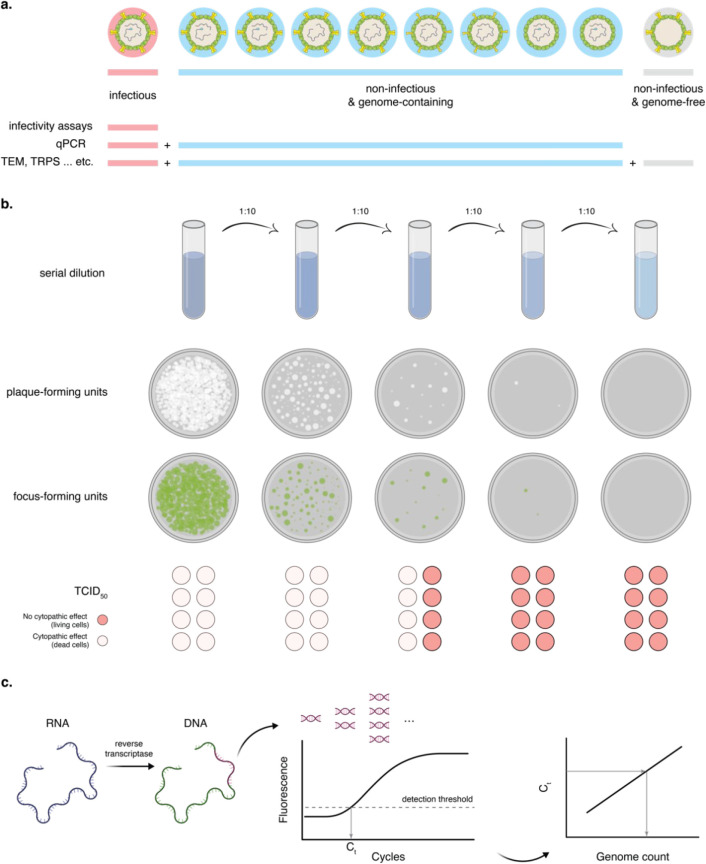
Figure 4.
Quantification of viruses. (a) Schematic showing the different populations that exist in a virus solution: infectious viruses, noninfectious/genome-containing, and noninfectious/genome-free. Different quantification methods, e.g., infectivity assays, qPCR, and TEM, will assess different populations. (b) Schematics showing three different ways to express the concentration of infectious viruses: plaque-forming units, focus-forming units, and TCID50. (c) Schematic showing RT-qPCR to determine the genome count of viruses. The RT, i.e., reverse transcriptase, step is only needed for RNA viruses. Viruses containing incomplete genomes that have the segment being replicated in the PCR will still be counted: the contrary also applies; viruses containing incomplete genomes that do not have the segment being replicated will not be counted.