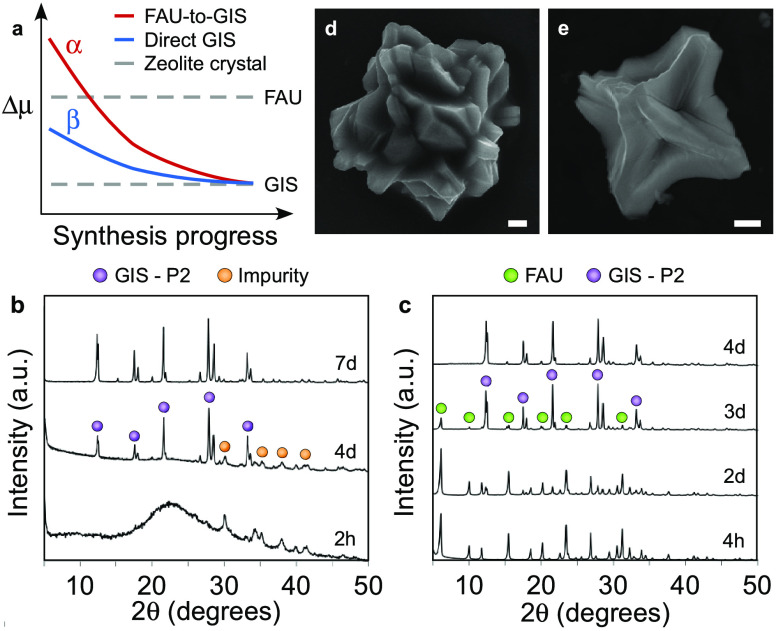
Figure 8.
(a) Hypothetical changes in chemical potential, Δμ, with synthesis progress, adapted from the IZT concept proposed8 for different growth solutions (α and β) and zeolite products (FAU and GIS). Growth mixture α refers to the nominal synthesis condition resulting in a FAU-to-GIS transformation. Growth mixture β is the supernatant of the previous mixture extracted at a time corresponding to full FAU crystallinity prior to the onset of GIS nucleation, where continued heating results in direct crystallization of GIS. (b, c) Time-resolved powder XRD patterns of solids extracted from growth mixtures β (b) and α (c). Select peaks of FAU, GIS-P2, and impurity phases are indicated by green, purple, and orange circles, respectively. (d, e) Scanning electron micrographs of GIS-P2 products obtained after 7 days of hydrothermal treatment of growth mixtures (d) α and (e) β. Scale bars represent 1 μm.