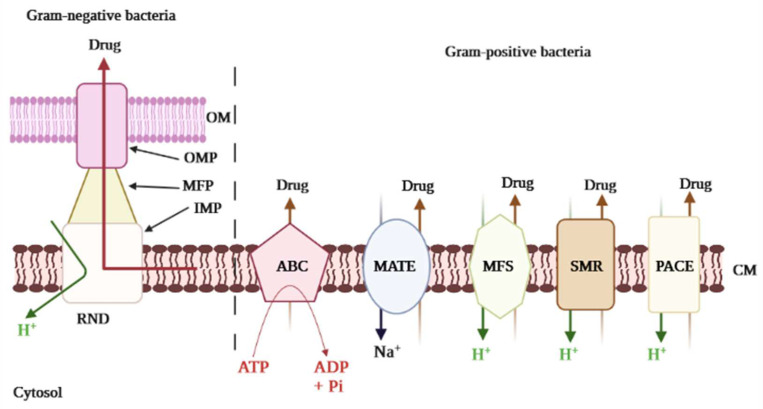
Figure 1.
Major efflux pump systems in bacteria. The major efflux pump family, namely ABC (ATP Binding Cassette), MATE (Multidrug and Toxic Compound Extrusion), MFS (Major Facilitator Superfamily), SMR (Small Multidrug Resistance), RND (Resistance Nodulation and Cell Division), and PACE (Proteobacterial Antimicrobial Compound Efflux) are represented. The specificity of Gram-negative bacteria is shown with the presence of the OM (Outer Membrane) in addition to the CM (Cytoplasmic Membrane). The components of RND are OMP (Outer Membrane Protein), MFP (Membrane Fusion Protein), and IMP (Inner Membrane Protein), making the tripartite conformation. The primary transporters use energy derived from ATP hydrolysis (ABC), whereas the secondary transporters use the energy from the H+ motive force or the Na+ electrochemical gradient.