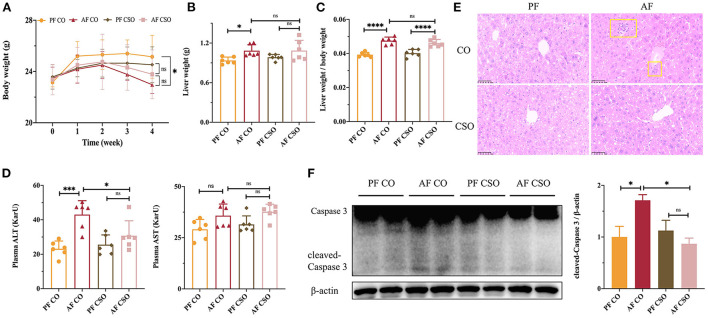
Figure 1.
Dietary CSO supplementation rescues alcohol-induced liver injury. (A) The body weight. (B) The liver weight. (C) The ratio of liver-to-body weight. (D) The activities of plasma ALT and AST. (E) H&E staining (400×). (F) The expression of hepatic cleaved-Caspase 3. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 indicate statistically significant.