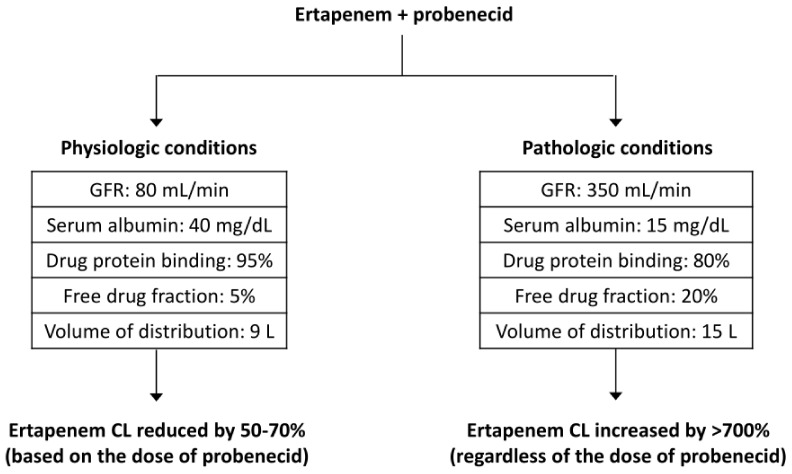
Figure 1.
In physiologic conditions (left side), concomitant administration of probenecid resulted in a dose-dependent reduction (50–70%) in the clearance (CL) of ertapenem. In pathologic conditions (right side), the presence of a severe hypoalbuminemia resulted in a 400% increase in the ertapenem free fraction available for renal excretion. This effect was amplified by the presence of augmented renal clearance (400% increase in the glomerular filtration rate, GFR). Moreover, the patient also gained 6 L of fluids, further diluting the concentrations of ertapenem (the volume of distribution increased by 40%). The net result is a severe reduction in the CL of ertapenem related to the pathological conditions associated with ICU which greatly outweigh the effect of the pDDI related to concomitant probenecid administration.