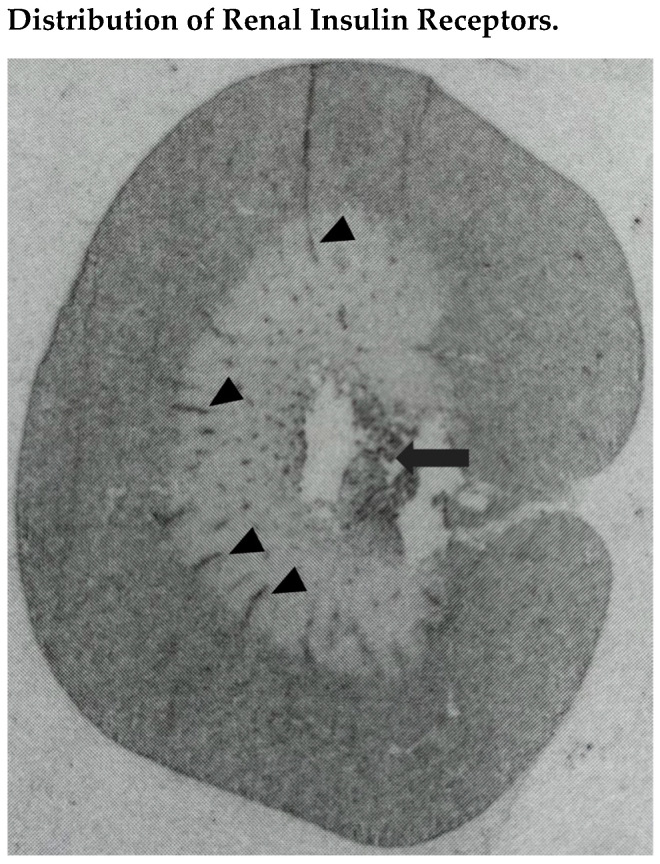
Figure 1.
In situ-autoradiography showing distribution of radiolabeled insulin binding sites in the kidney of a normal Wistar-Kyoto rat. Insulin binding was greater in the renal cortex, where it was comparable in tubules and glomeruli that could not be distinguished from the surrounding tissue. In the renal medulla, radioligand binding was detected primarily in longitudinal structures crossing the outer portion, presumably corresponding to interlobar vessels (black arrowheads), and the inner portion, presumably corresponding to hilar fat (black arrow).