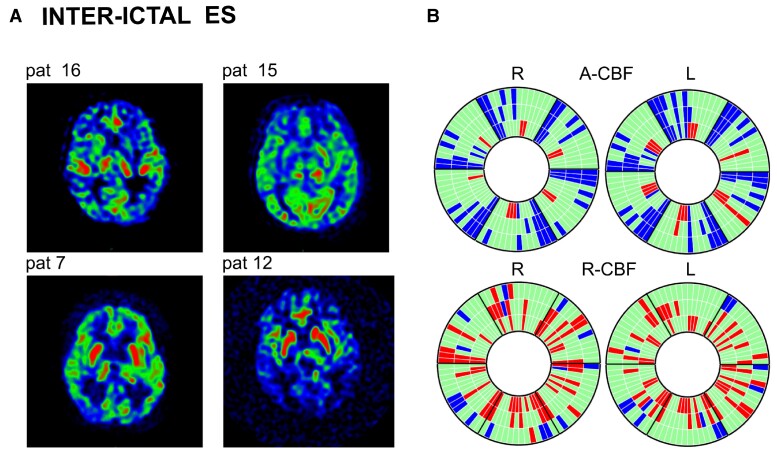
Figure 5.
Inter-ictal ASL-MRI in patients with epileptic spasms (Group 3). (A) ASL-MRI in four representative patients with epileptic spasms (Patients 16, 15, 7 and 12). Patients 15 and 16: examples for A-CBF increase in thalamus and A-CBF decrease in cortex. Patients 7 and 12: examples for R-CBF increase in striatum and the R-CBF decrease in cortex. (B) Donut charts (for details, see Fig. 1B and Supplementary Fig. 5) including ASL-MRI examinations of all 14 patients showing significant A-CBF and R-CBF changes compared with controls in this group. A-CBF decrease in corresponding C-S-T, C-S, C-T or S-T compartments. A-CBF increase in T in four patients (10, 14, 15 and 16), all aged <1 year, in one of them (15) associated to homologous S or S-C A-CBF increase.