Table 1.
Summary of the antimicrobial effects of some plant-derived terpenoids, alkaloids, and flavonoids.
| Compounds | Chemical Structures | Target Microorganisms | Antimicrobial Effects | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terpenoids | 1,8-cineole |
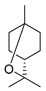
|
A. baumannii C. albicans MRSA strain E. coli |
Cell membrane destruction | [22] |
| cinnamaldehyde |
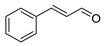
|
S. typhimurium E. coli O157: H7 P. fluorescence B. thermophacta S. aureus |
1. Cell membrane destruction 2. Anti-quorum sensing action 3. Inhibition of protein synthesis |
[23,25,30,31] | |
| carvacrol |
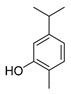
|
S. typhimurium E. coli O157: H7 P. fluorescence B. thermophacta S. aureus P. fluorescens KM121 |
1. Cell membrane destruction 2. Anti-quorum sensing action 3. Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis 4. The synergistic effect 5. Inhibits cell movement and bacterial invasion |
[23,26,27,29,32] | |
| thymol |
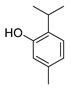
|
S. typhimurium E. coli O157: H7 P. fluorescence B. thermophacta S. aureus P. fluorescens KM121 |
1. Cell membrane destruction 2. Anti-quorum sensing action 3. Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis 4. The synergistic effect |
[23,26,27,28,32] | |
| eugenol |
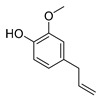
|
S. typhimurium E. coli O157: H7 P. fluorescence B. thermophacta S. aureus |
1. Cell membrane destruction 2. Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis 3. The synergistic effect |
[23,27,28,32] | |
| limonene |
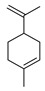
|
A. baumannii C. albicans MRSA strain E. coli |
Cell membrane destruction | [23] | |
| oleanolic acid |
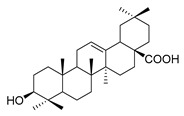
|
E. coli
S. aureus Enterococcus faecalis P. aeruginosa |
Antibacterial | [33] | |
| Alkaloids | piperine |
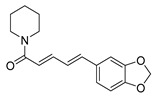
|
S. aureus B. subtilis Salmonella sp. E. coli |
Efflux pump inhibition | [34,35] |
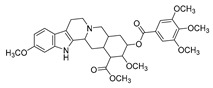
| reserpine |
|
E. coli | Efflux pump inhibition | [36] | |
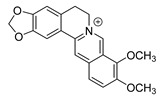
| berberine |
|
E. coli Micrococcus luteus P. aeruginosa Prevotella intermedia Fusobacterium nucleatum MRSA strain |
1. Efflux pump inhibition 2. DNA-intercalating 3. Growth inhibition |
[37,38,39] | |
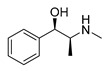
| L-ephedrine |
|
Influenza A virus | DNA-intercalating | [40] | |
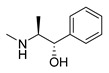
| D-pseudoephedrine |
|
Influenza A virus | DNA-intercalating | [40] | |
| L-methylephedrine |
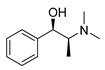
|
Influenza A virus | DNA-intercalating | [40] | |
| chelerythrine |
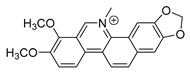
|
S. aureus MRSA strain ESBLs-SA |
1. Nucleic acid synthesis and repair inhibition 2. Growth inhibition |
[41] | |
| 8-hydroxy quinoline |
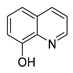
|
S. aureus
H. influenza S. pneumoniae |
Permeability change of membrane | [42,43] | |
| michellamine b |
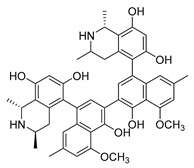
|
HIV | Protein activity inhibition | [44] | |
| sanguinarine |
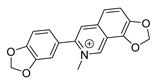
|
K. pneumoniae MRSA strain P. aeruginosa Streptococcus pyogenes |
1. DNA-intercalating 2. Growth inhibition |
[45,46] | |
| roemerine |
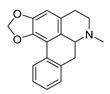
|
S. aureus
B. subtilis |
1. Efflux pump inhibition 2. Permeability change of membrane |
[47,48] | |
| dihydrochelerythrine |
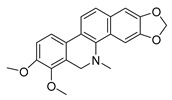
|
S. aureus MRSA strain |
Growth inhibition | [49] | |
| evodiamine |
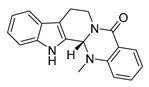
|
M. tubercolosis | Peptidoglycan biosynthesis inhibitor | [50,51] | |
| Flavonoids | hesperidin |
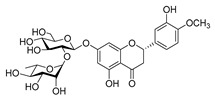
|
S. aureus
L. monocytogenes |
Inhibit bacterial growth by modulating the expression of virulence factors | [52] [53] |
| oroxylin a |
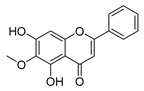
|
B. subtilis
S. aureus |
/ | [54] | |
| apigenin |
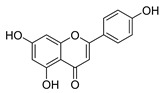
|
S. aureus
B. subtilis E. coli P. aeruginosa. |
1. Inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis 2. Increases cell membrane permeability |
[55] | |
| morin |
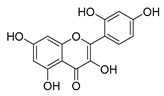
|
E. coli | Inhibition of ATP synthetase | [56] | |
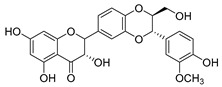
| silymarin |
|
E. coli | Inhibition of ATP synthetase | [56] | |
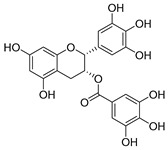
| epigallocatechin gallate |
|
S. maltophilia | Inhibits dihydrofolate reductase | [57] | |
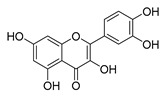
| quercetin |
|
P. aeruginosa | 1. Inhibits viral polymerase and viral nucleic acid 2. Inhibits the formation of its biofilm |
[58] | |
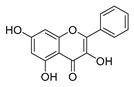
| galangin |
|
S. aureus | 1. Destroys the plasma membrane 2. Weakens the cell wall |
[59] | |
| catechin |
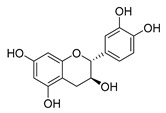
|
B. subtilis
E. coli |
Inhibits the bacterial DNA gyrase | [60] [61] |
|
| baicalin |
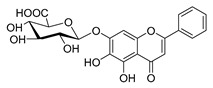
|
Salmonella spp. Staphylococcus spp. |
Inhibits biofilm formation | [62] [63] |
|
| phloretin |
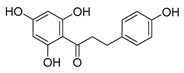
|
C. albicans | 1. Inhibits the pathogenicity 2. Inhibits virulence factors |
[64] | |
| silybin |
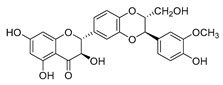
|
MRSA strain | Inhibits the efflux pump | [65] |
