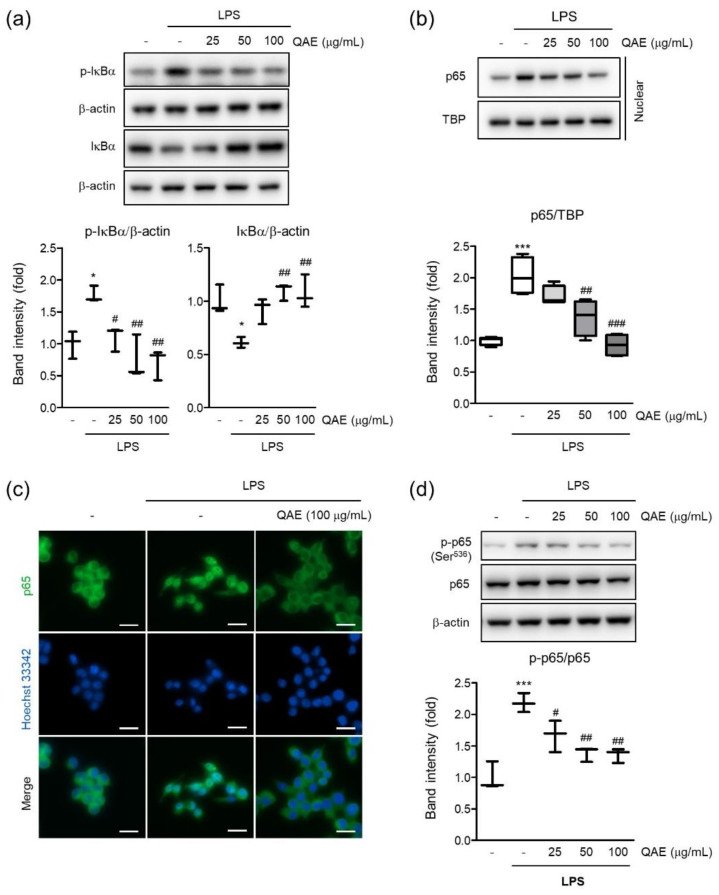
Figure 4.
QAE inhibits the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. After QAE pretreatment (25–100 μg/mL) for 3 h, BV2 microglial cells were exposed to LPS (100 ng/mL) for 1 h. (a) Phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα. Equal protein loading was verified by β-actin immunoblotting (n = 3). (b) p65 expression in nuclear. Equal nuclear protein loading was verified by TATA-box binding protein (TBP) immunoblot (n = 4). (c) Immunocytochemistry. After treatment, cells were immunostained with an anti-NF-κB (p65) antibody and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated secondary antibody. Scale bar represents 25 μm. Hoechst 33342 was used for nuclear counterstaining (n = 3). (d) Phosphorylation of p65 at Ser536. Expression of phosphorylated p65 was normalized with expression of total p65 immunoblotting (n = 3). Significant versus control, * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001; Significant versus LPS alone-treated group, # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001.