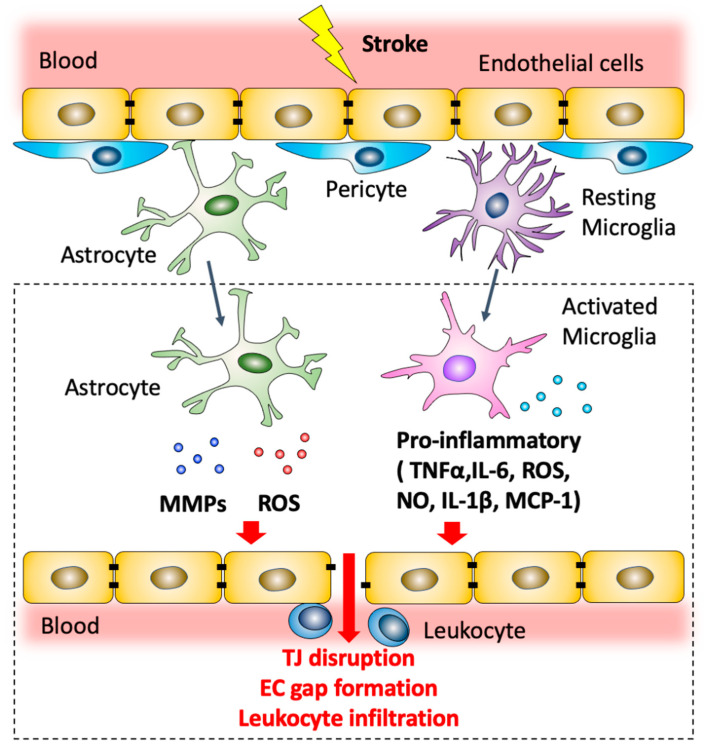
Figure 2.
Modulation of blood–brain barrier permeability by astrocytes and microglia after ischemic stroke. Post-ischemic astrocytes produce MMPs and ROS that contribute to TJ disruption and endothelial cell gap formation. Microglial cells are polarized to a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Pro-inflammatory microglia can produce a variety of mediators including NO, ROS and pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, which contribute to downregulation of junctional complexes between adjacent brain endothelial cells and lead to BBB dysfunction. Activated microglial cells also secrete MCP-1 which promotes leukocyte recruitment.