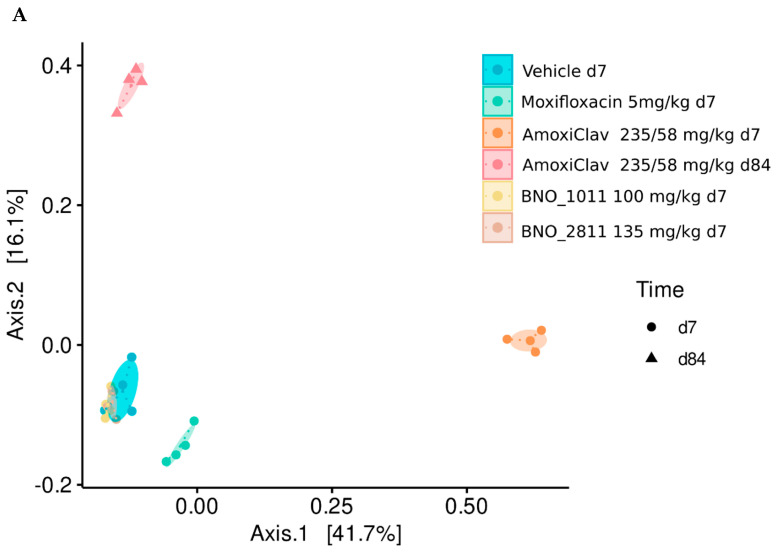
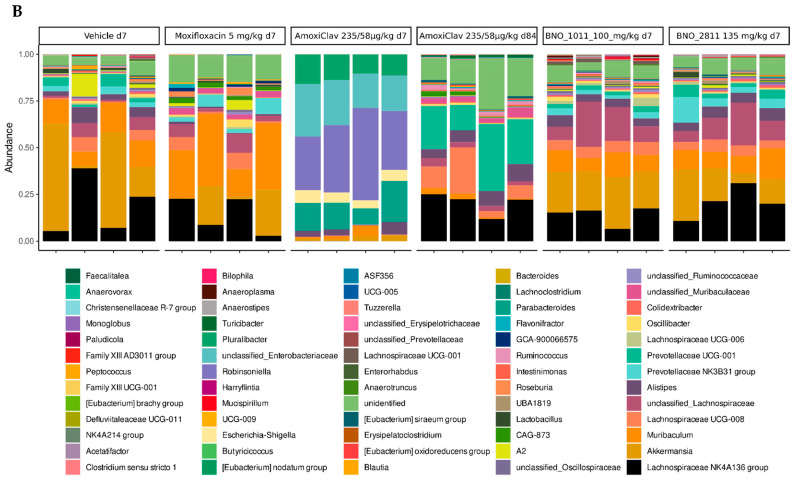
Figure 1.
Changes in microbiome after treatment of mice with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (day 7 and 84), moxifloxacin (day 7), BNO 2811 (day 7), or BNO 1011 (day 7), compared to a control group (water). (A) Similarity between individual bacterial compositions were studied using principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) of 16S rRNA gene sequencing data. Individual samples (colored dots) clustered well, according to the treatment groups. Ellipses represent the 95% confidence intervals, based on a multivariate t-distribution for each group. The center of each group is marked by small dots. Differential clustering of treatment groups after PCoA indicates compositional shifts after seven days of antibiotic treatment with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (orange dots). Additional shifts of bacterial compositions 11 weeks after discontinuation of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (d84, red triangles) point to a long-term damage of the microbiome, due to the antibiotic treatment. Bacterial compositions of mice treated with BNO 1011 and BNO 2811 showed high similarity to untreated mice, inferring no impact on the intestinal microbiome. Coordinates represent 41.4 and 16.1 percent variance of the dataset. (B) Taxonomy bar plot illustrating relative abundances of detected bacterial genera in samples and treatment groups.