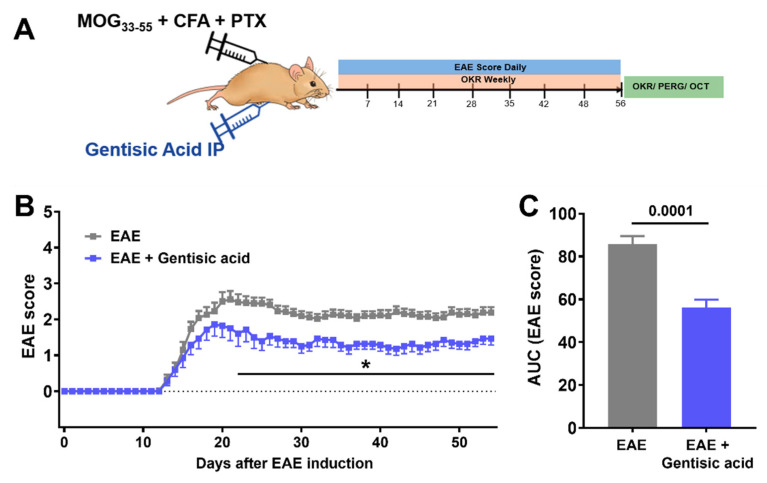
Figure 3.
Systemic gentisic acid (GA) administration reduces clinical severity in MOG-induced EAE: (A) Overview of animal study design including EAE induction in 52 female C57BL6/J mice and in vivo readouts. Twenty-six EAE mice received weekly intraperitoneal (ip) administration of 50 mg/kg GA. All animals underwent daily EAE scoring, weekly assessment of visual acuity, and pattern ERG recordings and OCT imaging 56 days after EAE induction. (B) Untreated EAE mice (grey = EAE) displayed a moderate course of motor sensory impairment over time. Systemic GA administration in EAE animals (blue = EAE + GA) mitigated motor-sensory deficits and resulted in a significantly milder disease progression. Mean scores per day with SEM are given and * indicates p < 0.05 in EAE vs. EAE + gentisic acid treatments. (C) Analysis of area under curve (AUC), as the sum of individual EAE courses per group, confirmed a significantly milder overall disease progression in GA-treated EAE mice when compared to untreated, vehicle-administered EAE animals.